Compared to indoor plants, flowers in the country are much easier to grow. They do not require as many fertilizers and minerals, since most of the nutrients are taken from the soil. Of course, the use of various fertilizers speeds up the growth of any plant. If we are talking about flowers in the country, then it is better to fertilize them in the spring, but it is also possible at other times.
Each plant variety requires an individual approach. The main thing is not to overdo it with fertilizers. Too much of them stimulates foliage growth by reducing flowers. In this article we will describe in detail all the care options and figure out what you can feed the flowers with in the spring.
Flowers at the dacha
In a suburban area you can grow different varieties of flowers. But they are all divided into two types: perennial and annual. Perennial flowers are not so demanding of additional fertilizers and feeding , since their root system is already formed and the plant constantly receives useful substances and fertilizers for active flowering from the soil.
With annual flowers it is a little more difficult. Every spring they go through the process of planting or breaking through the soil from seeds. Annual flowers are plants that grow, produce seeds, and die during one growing season. Depending on the type, annual plants can be transplanted anywhere on the site, regardless of the time of year. As a rule, annual flowers are used to form small flower beds, borders, and even plant them in hanging vases.
How many times should you feed flowers in spring?
The frequency of fertilization depends on the growth stages of the flower, as well as the length of its life cycle.
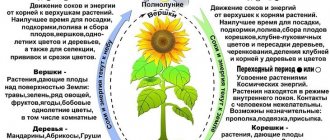
For perennial plants, it is necessary to fertilize three times in the spring. The first in line to receive nutrients are roses, crocuses, tulips and hyacinths. Actions can be taken as soon as the snow cover is completely gone. The second feeding is recommended at the moment of flowering. This time usually falls in May-June. The time of the third comes after the cessation of flowering. It is important not to skip the third feeding, as it will be the key to successful wintering of flowering plants.
The feeding scheme for annuals differs due to the time of their life cycle. For annual flowers, applying nutrient mixtures twice is sufficient. The first is produced fourteen days from the moment of planting at the chosen place of growth. Repeated feeding is done as soon as the plant begins to bloom.
Ventilation or soil drainage
There shouldn’t be any particular issues with the soil itself. It is best if it is black soil. But drainage for flowers is very important, especially in spring. Drainage is critical, especially after winter, otherwise the plants may suffocate and begin to rot due to lack of air circulation around the roots. Soil drainage is improved by adding 5-8 cm of organic material.
We remove a similar amount of compacted soil, carefully, without damaging the roots, and add compost, peat moss, chopped bark or manure in slightly larger quantities (since over time the fluffy material will also settle). If the soil is poorly compacted or clay based, 3-5cm of sand added along with organic material will further improve drainage.
What elements do flowers need?
For development, growth, and flowering, domestic flowering and decorative foliage plants require the following elements:
- potassium increases resistance to cold, helps to absorb certain microelements, and is responsible for flowering;
- phosphorus - the element is responsible for the process of plant development and for flowering, which, if it is deficient, may not occur at all or will not be very abundant;
- nitrogen is necessary for the development of foliage, without it the leaves lose their color and fade (an excess of nitrogen leads to a lack of flowering);
- calcium is involved in nitrogen and carbon metabolism, and its deficiency prevents young leaves from developing and weakens root growth;
- sulfur is important for leaves, which without this element will begin to wither;
- Magnesium is responsible for photosynthesis, so if it is deficient, the leaves turn pale.
In addition, elements such as boron, copper, manganese, molybene, and iron are no less important for home flowers.
Watering
Watering flowers in the spring should be done very carefully, since the soil is still quite damp after the winter snow has melted, although it may look dry on top. However, almost all flowers require regular watering, especially in warm weather.
But it is worth considering the fact that “overwatering” contributes to the development of diseases such as rot and fungus in particularly damp soil. So you shouldn’t water flowers in the spring more than once a week. It is necessary to water from a minimum height to the very roots, and not to spray water from a watering can on the leaves and flowers.
If the number of flowers in your area is very large, use special drip irrigation hoses. All water procedures must be performed in the morning so that direct sunlight does not evaporate the moisture too quickly.
How often should you water indoor flowers? It all depends on the variety and specific species. The website “Sadim.Guru” presents a huge number of articles on various types of indoor plants; just use the search.
Deadlines
When feeding outdoor plants, adhere to the deadlines. Nitrogen preparations are applied in the spring, since in the fall it stimulates root growth. During the winter they may freeze and the plant will die. At the end of August or September, products with potassium and phosphorus are used. Nutrients are especially important for long-flowering garden inhabitants.
The easiest way to care for annual flowers is considered. The drug is applied 2 weeks after planting and in July. During this period, buds begin to form. Perennial plants are fed more often: in the spring, during budding, after flowering.
Autumn feeding is just as important as spring feeding. They lay the foundation for the formation of buds and saturate the soil with useful substances. Fertilizers for street and indoor flowers consist of similar components. The main difference is that it is better to fertilize indoor flowers with complex preparations, and garden flowers with products containing one substance.
Complex fertilizers are not used until the snow melts. The earth does not warm up and nutrients are not absorbed into the root system.
To ensure that the plants in the garden always delight with bright colors from spring to late autumn, fertilizers must be used.
Fertilizer
Timely application of plant fertilizers to the soil, especially during planting, will provide sufficient nutrients for any variety of flowers for several weeks. After about a month, fertilizer can be applied again. Fertilizers are applied for the third time already in mid-summer, if they are needed (individually for different varieties).
Note!
General purpose granular or liquid fertilizers will work equally well for all flowers in the garden. Although liquid fertilizers are better suited for annual plants that have only recently appeared in the flower bed from seeds or after transplanting from a nursery.
Before using any type of mineral fertilizer, carefully read the label to determine the rate and dose for each specific plant. Use fertilizers sparingly, working them only into the soil rather than spraying them onto the foliage. After applying fertilizer, the flowers must be watered, as the concentrated composition can burn the roots. The best option would be to dilute the fertilizers in water in advance.
Ways to feed flowers
The large number of types of flower crops forces one to resort to different types of fertilization.
According to the method of adding nutrients, they are distinguished:
- Root;
- Foliar.
Most often, gardeners apply fertilizers at the root in liquid or dry form. Mineral fertilizers can be used in dry form (in a planting hole or can be embedded in the top layer of soil) or in dissolved form with irrigation water. Organic fertilizers, such as manure and bird droppings, are often applied in the form of infusions, and compost, peat and humus are used to mulch and fill the planting hole.
Foliar feeding by leaf is often underestimated, although this method of fertilizing helps to quickly provide the plant with the necessary micro- and macroelements. For weakened, sick, damaged and young plants, this method is optimal. For foliar feeding, special fertilizers or conventional complex preparations are used, but in a lower concentration than when applied with irrigation water.
Long-acting fertilizers, which are available in the form of sticks, pyramids or granules, deserve special attention. They gradually release nutrients, maintaining the desired concentration of micro- and macroelements.
The validity period of some drugs is more than a month, which relieves the gardener of the need to frequently feed plants that require increased doses of nutrients.
Using mulch
Mulch is useful for many flowers, as it retains moisture well in the soil and prevents the roots from heating up on hot days. In addition, mulch helps control weed populations. But such a fertilizer is not particularly suitable for indoor flowers in ordinary home conditions.
It is best to use organic mulch, as any inorganic material will heat up significantly, first burning the plant and then transferring all the accumulated heat to the soil. It is best to use bark shavings, pine needles, dry compost or just dry grass. The height of the mulch layer should not exceed 7-8 cm, since a larger layer will contribute to an increase in populations of slugs and other harmful insects.
Using compost as a basic fertilizer
The easiest way to keep your flowering garden in top condition is to add a certain amount of compost to the soil each spring. Spread the compost evenly over the surface of the ground in a layer of about 10 cm, as soon as all the snow has disappeared from the ground and it has dried out a little.
By performing this simple procedure every spring, the amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other chemical compounds required by plants will slowly be released into the soil. Thus, you will not have to resort to additional fertilizing methods for a long period of time, and such flower feeding in the spring will be very useful.
Instead of compost, you can use fresh manure mixed with granular all-purpose fertilizers, which are sold at any farm store. These activities will encourage new, healthy growth in the spring, when plants are most in need of additional nutrients. Store fertilizer on the leaves and water well after application.
Organic fertilizers and their use for flowers
Organic fertilizers can be called the most natural fertilizer, because they are products of decay or vital activity of living organisms:
- Manure;
- Bird droppings;
- Compost;
- Humus;
- Peat;
- Sawdust;
- Green manure.
Organic matter is well absorbed, but when choosing the optimal option, it is necessary to take into account the species characteristics of plants, because not all flowers react normally to bird droppings or compost, and peat and sawdust acidify the soil, which is unacceptable when growing calciphiles.
Natural plant food
Compost, humus and cut green manure can be used for all flower crops. It is best to mulch the soil of flower beds and flower beds with them, adding a little natural humus. Regular renewal of the mulch layer in some cases completely replaces other organic fertilizers, and weed infusions are also an excellent source of microelements.
In addition to replenishing nutrients, organic substances such as humus, compost, peat and sawdust improve the structure of the soil, making it looser and more breathable.
Required tools and materials
To care for flowers in your country house or suburban area, you will need standard gardener tools, namely:
- Bayonet shovel.
- Rake.
- Garden shears, pruning shears or small lopper.
- Weeding knife.
- Watering hose.
- Several buckets.
- Watering can.
- Spray.
- Punch.
- Gardening gloves.
- Cultivator.
Spring fertilizers - how and what to apply
Spring application of fertilizers on the site and dacha
Everything we plant grows well only on fertile soil. And when the soil lacks nutrients, you cannot expect a bountiful harvest and beauty.
Vegetables and annuals are usually fertilized during the process of growing seedlings and immediately after “moving” to beds and flower beds.
It is important to feed perennials, fruit trees, ornamental trees and bushes when replanting, but you should not keep them on a starvation diet during the season.
Each season has its own “diet”, because different periods of the growing season require a certain ratio of basic nutrients.
Spring fertilizers based on nitrogen, which is responsible for active growth.
No less important in the spring are phosphorus, which stimulates root growth, and potassium, which supports flowering and lays the foundations for fruiting.
In autumn, the last two components predominate in fertilizing and fertilizers; they help plants prepare for the winter cold and survive it safely.
Each summer resident has his own preferences.
The older generation usually uses natural organic matter, which in its “fresh” form inhibits the soil microflora and can even burn the roots and also contains pathogens and weed seeds.
Therefore, it needs to be “brought to mind”: the manure needs to be rotted, and the compost needs to ripen.
A good alternative to old-fashioned fertilizer is ready-made organic fertilizers, environmentally friendly and practically free of disadvantages. You can purchase them in specialized stores.
Organomineral fertilizers begin to work to increase fertility immediately after they are applied to the soil.
They help structure the soil, increase the amount of humus in it and increase plant resistance to many bacterial and fungal diseases.
New generation mineral fertilizers, as a rule, are designed for specific crops or problem areas of these crops.
In fertile soil they are quickly absorbed by plants.
“Sticks” do not require special care, have a prolonged effect and gradually release nutrients when watered.
Dry water-soluble fertilizers contain a full range of macro- and microelements necessary for flowers, ornamental plants, vegetables and berries, and finally, new forms of liquid root and foliar fertilizers are the most gentle for soil microflora, usually contain humates and, in fact, are both and fertilizers and growth stimulants.
However, if you want to achieve noticeable results, you should not “brush everyone with the same brush” - each crop (species or family) needs its own diet.
Related link: What types of fertilizers are there and how to prepare them yourself
For example, decorative leaf plants need a large amount of nitrogen, while flowering plants need potassium, which ensures long flowering.
Important: many plants have a capricious character and do not tolerate even minimal errors in the diet, so before purchasing fertilizers, study the tastes of your pets.
In addition to nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, which form the basis of the diet, plants need microelements, preferably in chelated form.
These drugs are especially useful for those who are developmentally delayed.
But before choosing a fertilizer, determine which element is missing in the soil and which “additive” will be optimal.
Growth stimulants and regulators (see the link for more details) strictly speaking, do not belong to fertilizers, but they are vital for plants, since they help to safely survive all the vagaries of the weather.
They accompany plants from the appearance of the first shoots to the formation of ovaries, accelerating the growth of stems and foliage and making flower ovaries more viable.
Fertilizers in spring - norms and rules for application
The spring season is considered the most favorable for applying all types of fertilizers to the soil. This applies primarily to planting new plants that need to create a supply of nutrients, however, feeding already mature plants is extremely important for their normal growth and development. Fertilization is especially important for fruit, berry and vegetable crops. Today there are many fertilizers, fertilizers and protection products. Of course, on each package you will find comprehensive information on this fertilizer, but it is very important to understand the general principles of the action of fertilizers.
Kaoke fertilizer to choose for spring application
If we talk about organic fertilizers, such as manure or humus, peat, bird droppings and compost, they are recommended to be applied once every two to three years.
The main advantage of such fertilizers is the ability to enrich the soil with useful microelements. They necessarily contain phosphorus, nitrogen, calcium, potassium and other elements that have a positive effect on the condition of the soil and contribute to plant nutrition. Organic matter loosens the soil very well, improves its structure and is environmentally friendly. However, not all owners of cottages or summer cottages are ready to put up with the dirt and smell that accompany organic matter.
As for mineral fertilizers, they need to be applied to the soil annually. Despite the fact that mineral fertilizers do not affect the improvement of soil structure, there is no need to be biased towards them. After all, thanks to mineral fertilizers, plants receive all the elements necessary for growth, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus. The advantage of mineral fertilizers is their ease of use; they dissolve in the soil without difficulty, which means they are more quickly absorbed by plants. They usually fertilize where there are the most roots that can absorb nutrients, i.e. not under the very trunk of the apple tree, but around the entire trunk, as far as the branches stretch. After sprinkling, fertilizers must be embedded in the ground.
Granular fertilizers are popular and convenient, but take longer to dissolve and affect plants. Powder and liquid will work faster, and they are usually better dosed and more balanced. This fertilizer is usually dissolved in water and either watered under the roots or sprayed onto the leaves using garden pumps or special sprayers.
The optimal spring norm for a 1-acre plot is considered to be adding to the soil: 200-250 g of phosphorus fertilizers, 200 g of potassium fertilizers (replaced with wood ash) and 300-350 g of nitrogen fertilizers (urea or urea, ammonium nitrate).
Recently, complex fertilizers are also considered very convenient, with two or even three components in their composition, which enrich plants with the necessary substances, including microelements. Now gardeners can choose special fertilizers for seedlings, ornamental deciduous, coniferous, flowering and other types of plants. All of them are balanced, without sediment, manufactured specifically for the needs of specific groups of plants, and are produced in liquid form.
Liquid fertilizers dissolve well in water and are used as root and foliar feeding. Liquid fertilizers are applied during sowing or planting, or along with water during irrigation. Granular nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied directly to the soil when sowing or planting seedlings, or before digging to a depth of approximately 20 cm.
It is important to remember that when applying organic, mineral and complex fertilizers, you must strictly follow the instructions on the packaging, because an excess dose can have an undesirable opposite effect on plants.
We hope that our tips will be useful when choosing fertilizers. Enrich your plots. We wish you success and great harvests!
Author E. Gorbacheva
vsaduidoma.com
Fertilizer for flowering plants
All plants need to be fed, no one can escape this rule. Providing the necessary substances (in the right quantities and at the right time) is a vital requirement for successful growth. Even fertile soil requires special additives.
Plants take hydrogen, carbon and oxygen from water and the atmosphere, but get their nutrients from the earth. When the soil does not have enough strength, or weakens over time, the solution is to add fertilizer. This contribution should be calculated based on the needs of the plant and soil characteristics.
How to choose the best mineral plant fertilizer? By composition. Consider the main components: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. What to look for: The percentage of each nutrient is listed on the package using the abbreviation NPK. For example, the mark 10:5:5 means that the fertilizer contains 10% nitrogen (N), 5% phosphorus (P), 5% potassium (K). A fertilizer that supplies these three types of nutrients is called “complete.”
Fertilizers also contain secondary nutrients such as calcium, sulfur, iron, zinc and others. Criteria for choosing additives: plant variety, development period, its condition and preferences.
Advice from gardeners regarding composition also boils down to the preference for formulas without nitrates and chlorine.
If you can't test the soil or understand what a particular plant needs, you can buy a balanced fertilizer, such as 10:10:10, which contains equal amounts of each of the main three ingredients.
Fertilizer that contains more nitrogen is beneficial for the growth phase. If there is more phosphorus and potassium, this is the right choice for the flowering period.
The modern market offers so-called RA “boosters” (flowering stimulants). A type of fertilizer containing only phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), the two most important elements for flowering. Experienced gardeners note that such a formula without nitrogen does not provide complete nutrition, so it is recommended only as a supplement for two to three weeks in the final stage of flowering.
In addition to mineral nutrients, there are organic ones intended to enrich the earth. These are compost, ash, sawdust, manure and other means. They do not contain NPK elements, but are required for plant care.
Is it possible to replace mineral fertilizers with organic ones? It will be cheaper in price and more practical in consumption. But the replacement should not be permanent; these types of fertilizers perform different functions.
There are formulations on the market with mineral and organic compounds called organomineral fertilizers. This is the most complete form of nutrition.
Types by chemical composition
How to feed dahlias for growth and flowering
Based on their constituent components, fertilizers are divided into several types: alkaline, acidic and neutral. Each is suitable for a specific soil type.
Alkaline
Alkaline products consist of a complex of minerals and macroelements. They are well accepted by plants and quickly dissolve in water. The most common means are nitraboron and saltpeter. Their main task is to ensure intensive growth during the growing season, nourish the root system, and restore the immunity of home crops. What effects do alkaline components have?
- stimulate the growth of the root system;
- improve membrane development;
- regulate metabolism;
- increase resistance to adverse conditions;
- accelerate the process of flowering and fruiting;
- improve soil quality.
Alkaline products for flowers
Important! Alkaline agents prevent cell death and growth retardation.
Sour
Acidic fertilizer components are widely used for soils with a low acidity percentage. These include the following microelements:
- ammonium chloride;
- urea;
- ammonium nitrate;
- superphosphate.
Acidic products are free-flowing. They penetrate the soil as quickly as possible, enrich it with the necessary elements and accelerate the growth of seedlings. Acid fertilizers have undoubted advantages - a long shelf life and economical use, which allows you to significantly save your budget.
Neutral
Such fertilizers contain 1-2 main components and are suitable for use for many crops. Most often it is ammonia or nitrogen. They provide quick access of moisture to the root system of plants, fertilize the soil with useful minerals, accelerate the growth of crops and strengthen their immunity.
Note! It is recommended to apply neutral products before the growing season of the plant - in early spring. It is better not to use them in the autumn.
Types by release form
All fertilizers come in different forms. Each of them has its own characteristics and functions.
Liquid
Home indoor flowers blooming all year round
Liquid products are the most popular for treating houseplants. They are presented in the form of a solution of a homogeneous mass, which contains nutritional and mineral components in the composition. However, such preparations are highly concentrated and therefore need to be diluted with clean water.
Liquid preparations can be organic and mineral: the former are created from natural waste, the latter are prepared on the basis of chemical elements. Organic solutions have a mild effect on the root system of crops, but there is a drawback - an unpleasant odor.
Mineral gels are distinguished by their accuracy and speed of action. They are designed for specific dosages and are used in courses. All indoor flowers immediately absorb them, and productive results are observed within 2-3 days.
Important! Mineral preparations have their drawbacks - the possibility of overdose and burns of the root system.
Granular
Such fertilizers are widely used for processing vegetable crops in the garden and indoor flowers.
Granular treatment products
The product itself is in a porous capsule; it becomes available at high humidity. Granulated products are highly concentrated, so they are used 1-2 times a year: when crops need to bloom and in the cold season. The solution is scattered on the surface of the earth so that it surrounds the stem of the plant.
In the form of plates (tablets)
Soluble drugs are sold in the form of tablets or wafers. They need to be diluted with water for processing. The products have a strong concentration, which is why they are used with caution. The advantage of this form of release is that there is no overpayment for the liquid component of the fertilizer, which takes up about half of its mass. Tablet products are used before the growing season. When spraying, precise dosage must be observed to avoid burning the root system. Usually use 1 tablet of solution per 1 liter of liquid.
When to feed and water indoor plants
Fertilizers for plant crops need to be applied during the active growing season. At this time, growth of the root system and inflorescences is observed. Most domestic flowers are actively fed and watered in the spring and summer. However, there are other crops that require year-round fertilization. They develop throughout the year and bloom both in warm and cold seasons.
Fertilizers for home flowers
Spring and summer are the time for active feeding and watering of all domestic crops. The beginning of health procedures falls in March, the end of feeding - in the beginning or mid-September. With autumn and winter procedures, things are more complicated. If the plant has stopped blooming and stopped growing, then preventive feeding is not needed. Fertilizers and regular watering will be required if growth slows and the inflorescences persist.
Soil for flowers - improvement with mineral fertilizers
Mineral (chemical) fertilizers are sold in specialized stores. Methods of their use are described on the packaging.
The main thing is not to overdo it with an overdose, because... this leads to the accumulation of chemicals on vegetables, which negatively affects the environment and therefore human health.
- Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen starvation leads to slower growth of roots, leaves and shoots. Usually observed on sandy soils and in areas where a lot of organic fertilizer has been applied. To restore the nitrogen balance in the soil, nitrogen fertilizer is applied, oddly enough.
- Calcium (CA) Plant foliage suffers from calcium deficiency. The leaves begin to curl upward and as a result, the top of the plant dies. It is usually observed on acidic soils and is eliminated by liming.
- Magnesium (MG) If there is not enough magnesium, then the leaves begin to fall. This can be eliminated by feeding with magnesium sulfate.
- Iron (FE) If iron is insufficient, foliage is affected. It first turns yellow, then dries, and then falls off. Iron-containing fertilizers help combat this problem. This feeding must be done annually.
- Phosphorus (P) Phosphorus starvation is similar to nitrogen starvation, but the edges of the leaves seem to be burned. Typically found on clay and acidic soils. Eliminated with the help of root and non-root fertilizers.
- Potassium (K) Potassium deficiency leads to stunted plant growth. It is eliminated with the help of wood ash, which serves as mineral nutrition and helps against pests.