Lighting
The plant requires a lot of light, but its lighting should be diffused. Philodendron does not tolerate direct sunlight on its leaves . This causes burns in the form of dry yellow spots.
Varieties with green leaves can grow even in partial shade, while variegated forms require more intense lighting. You can read more about the types of philodendron and its placement in an apartment here; there is also a photo of the plant being cared for at home.
In nature, these vines are protected from the sun by tall trees. Therefore, almost all types of philodendrons with green leaves are very shade tolerant. They can exist even in the shade, although with a significant lack of lighting their leaves become smaller.
In winter, during the dormant period, philodendron may experience a lack of light . Lack of sun and short daylight hours often lead to greening of variegated philodendron varieties. Therefore, in cold weather, artificial illumination of the plant gives good results.
Botanical description
Philodendrons have an amazing variety of life forms: among them there are hemiepiphytes, epiphytes and even hemiepiphytes, but primarily philodendrons are climbing plants, epiphytes that use aerial roots to anchor themselves to a support. It’s not for nothing that in translation “philodendron” means “I love a tree.” If a philodendron seed has sprouted from the soil and there is no tree nearby to climb, the plant will crawl along the ground in a long vine, guided by the shadow cast by the nearest tree, fence, or anything else that the philodendron can use as a support. Philodendron has underground and aerial roots. Aerial ones are divided into numerous short and hairy ones, which serve to secure the plant to a support, and thicker and longer ones, used to extract nutrients and moisture.
- Pachypodium at home: care, types and varieties
The stems of philodendron are fleshy, woody at the base, the leaves are alternate, petiolate, large - in nature, sometimes up to two meters long. Depending on the type and variety, the leaf blade can be oval, pinnately dissected, arrow-shaped, etc. On the same plant, young and old leaves can differ not only in size, but also in shape. The color of the leaves is also varied, but the color of the upper side of the leaf is always darker than the bottom. The inflorescence of a philodendron is an ear with a waxy two-color blanket, similar to a hood, the fruit is a berry.
Some philodendrons grow to large sizes and require a lot of living space, so they are grown in greenhouses to decorate entryways, great rooms and conservatories. But we are interested in indoor philodendron, which will not take up much space and time, but at the same time will refresh and decorate an ordinary city apartment.
Temperature
This heat-loving plant does not tolerate low temperatures. But the intense heat doesn’t have the best effect on him either.
In summer, the flower must be kept at a temperature no higher than 25ºС , otherwise its leaves will dry out and fall off, despite high humidity.
In winter, the temperature can be reduced slightly , since during this period the speed of vegetation decreases sharply. But the temperature should not fall below 15ºС, otherwise the cold may destroy the flower.
Watering
Philodendron should be watered generously. It consumes and evaporates large amounts of moisture. Therefore, regular watering helps increase air humidity near the plant.
The soil should not be allowed to dry out completely , however, stagnation of moisture in the pot has a bad effect on the decorative qualities of the philodendron. Its leaves turn yellow from excess water. The optimal watering for it is one in which the top layer of soil (1 cm thick) sometimes dries out.
In summer, philodendron is watered 2 or even 3 times a week . In winter, watering is reduced, watering once every 7 or 10 days. The water should not be cold, settled or boiled.
Reviews
It grows quite quickly; at my work this vine grew more than 4 meters. In a very bright place, its leathery, spear-shaped leaves acquire a bronze tint. The wrappers of the young leaves are very beautiful - they are almost red. A completely unpretentious plant, suitable even for northern windows. In the summer I take him out to the balcony - he feels great there even in the heat. With a lack of moisture, the leaves wither slightly, but after watering the turgor is restored. It can grow like a vine or, if pruned, like a “bush.”
Svetlana Yurievna https://irecommend.ru/content/krasneyushchii-tsvetok
The plant is very unpretentious and very grateful, stubborn in its desire to survive and grow further))) It grows slowly - about 1 cm per year.
keygen https://otzovik.com/review_476964.html
Very unpretentious! Calmly tolerates low air humidity and short-term drying out of the earthen coma. If you give it nutritious, loose, slightly acidic soil and diffused light, then there will be no problems! A very grateful and responsive plant!
sweetsvetulia https://www.flowersweb.info/forum/forum44/topic102067/message3283387/#message3283387
Spraying
In summer, you need to spray the plant daily and wipe the leaves with a damp sponge. It is also useful to place the philodendron in the shower 1-2 times a week.
Water for spraying is taken at room temperature.
In winter, spraying is not carried out , since water entering the leaves at low temperatures contributes to the formation of rot.
In nature, philodendron grows only in very humid places. The apartment should maintain the highest possible humidity so that the plant does not lose its beauty. Air humidity should be maintained by spraying and spraying water near the philodendron.
Disease prevention and pest control
The indoor philodendron flower is resistant to fungal and bacterial infections and pests. The so-called nursing illnesses cause more trouble. Improper watering or lack of moisture, lack or excess of light lead to problems with leaves. Depending on the reason, they wither, turn yellow, and dry out.
- Overwatering can cause root rot to develop. The plant should be removed from the pot, shaken off and the wet soil washed off from the roots. Then you need to remove the rotten roots and plant the philodendron in fresh substrate. Optimizing your care will help you avoid problems in the future.
- Black dots may indicate mite or sooty fungus infestation. Philodendron is threatened by scale insects, mealybugs, and thrips. You need to remove pests with a damp sponge. The soil should be watered with an acaricide or systemic insecticide. This group includes strong drugs Aktara and Confidor.
Philodendron looks attractive due to the beauty of its leaves and the ability of its shoots to curl around a support or cascade. Decorative culture does not make high demands on conditions, but loves care and careful maintenance. Knowing the preferences of the plant, it is easier to avoid mistakes and preserve the beauty of the vine for many years.
The soil
The soil mixture for growing philodendron must be fertile, permeable to water and air, and moisture-absorbing.
It is recommended to use different soil compositions for plants of different ages.
For young plants, a mixture of 2 parts humus, 0.2 parts peat and 1 part mixture of charcoal and dry moss is suitable. Adult plants can be grown in a soil mixture of the same components, but taken in a 2:1:1 ratio.
Peat is an essential component in the soil mixture for philodendrons, since these plants prefer slightly acidic soil. In neutral soil they grow much worse. Alkaline soils should be avoided when planting philodendrons, as this will cause the plant to slowly die.
You can use another composition of the soil mixture:
- 3 parts of turf land;
- 1 part humus;
- 1 part peat;
- 0.5 parts sand.
But the easiest way is to buy specialized soil at a flower shop or garden center.
Recommendations
The flower can be grown from seeds, which are sold in flower shops. Or you can purchase an already grown plant there or in a greenhouse. The cost depends on the age of the flower and its size. So, a plant 35 cm high costs about 2,500 rubles, 80 cm - 4,500 rubles. Philodendrons 150 cm high cost about 40,000 rubles.
Philodendron is not a very difficult plant to grow. However, if there are errors in care, it is subject to attacks by pests and may lose its decorative effect. Its juice is poisonous, so philodendron should not be grown in areas where there are small children. When purchasing, you should refuse a specimen with yellowing leaves.
Fertilizer
For the proper development of philodendron, it needs regular feeding. The best fertilizers for it are complex mineral compositions, which contain potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus in equal proportions.
The plant needs to be fed from April to December . Fertilizers need to be applied every 2 weeks. At the beginning of January, feeding is stopped until spring.
Fertilizers are applied only to moist soil to prevent root damage and ensure uniform nutrient uptake. Therefore, fertilizing is carried out only after the main watering of the plant. It is very convenient to use liquid compositions for decorative deciduous varieties. They are diluted with water to obtain the desired concentration.
In addition to regular mineral fertilizing, you can feed the plant with organic fertilizers once a season . For philodendrons, it is enough to remove the top layer of soil 1-2 cm thick and put humus in its place.
Peculiarities
You need to know that philodendron sap is poisonous . When it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membrane, it causes pain, irritation, pain in the eyes and redness.
Therefore, all work on transplanting and pruning philodendron should be done with gloves . The flower itself must be installed in places inaccessible to children and pets.
There are types of philodendrons that are almost unsuitable for growing indoors. They are capricious, require very high humidity and a stable temperature of 20-25ºС.
Such species can only be purchased for keeping in a florarium. These are the golden-black philodendron, the decorated philodendron, and the warty philodendron.
Is it possible to keep a philodendron at home?
Superstitious and overly cautious gardeners do not recommend keeping philodendron at home.
The first category of such advisers is guided by signs. It is believed that philodendron is a “husband buster” plant that provokes quarrels and the subsequent departure of the spouse from the family. Especially in this regard, they slander the climbing philodendron, one of the most popular domestic species.
The second category of flower growers bases their beliefs on one simple fact: philodendron juice is poisonous . Therefore, if you are going to have such a tropical beauty at home, you should work with them with gloves so that the juice does not irritate the skin.
You should not believe in omens, but you must adhere to the main rule of all young parents and pet owners: keep the poisonous vine where children and four-legged pets cannot reach it. If there is no such inaccessible place where you could “hide” the philodendron, you should wait or refuse to purchase it.
But there are benefits from the poisonous vine: philodendron is on the list of plants that do the best job of purifying the air. In particular, they rid the atmosphere of formaldehyde and xylene.
Trimming / Support / Garter
Most types of philodendrons are hanging plants, the shoots of which can grow several meters in length.
To give the plant the appearance of a lush bush with many shoots, it is pruned.
Cut vines can be used for rooting, and the remaining parts will very soon sprout new shoots. This is how a plant of the desired configuration is formed.
To give the plant stability, special supports are used . These are soft columns by which the philodendron is held by its aerial roots. If the plant does not hold onto the support firmly, it can be tied to it with a rope.
General characteristics of the plant
The genus Philodendron includes about three hundred species of plants of the araceae family, growing in the tropical forests of South and Central America. For the most part, these are creeping vines with a herbaceous or partially woody stem. However, there are also tree-like forms, with a shortened stem from which a leaf rosette develops. These are, for example, species such as Sello and Philodendron doubly pinnate (double-pinnate). Almost all philodendrons develop aerial roots, thanks to which the plant attaches to trees and crawls upward towards the light.
Interesting fact! The life of these plants is closely related to trees, so their name comes from the Greek “philo dendron”, which means “tree-loving”.
Philodendron leaves come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. The diameter of the leaf plate ranges from a few centimeters to 1 meter. The shape can be round, heart-shaped, dissected, and the color is emerald, olive green, reddish. Philodendrons with deeply dissected leaves are very reminiscent of another tropical species - monstera. The main difference between Monstera and Philodendron is that the latter has a milky sap, while Monstera does not.
Monstera and Philodendron belong to the same family - araceae.
Under natural conditions, philodendron vines sometimes extend over distances of up to 200 meters. In a room, of course, a philodendron will never reach such an impressive size, but it is quite capable of weaving a window or wall.
Almost all philodendrons, with rare exceptions, need support.
In general, this plant is unpretentious and very decorative. It is grown in ordinary apartments, winter gardens, and especially large specimens decorate the halls and lobbies of institutions.
It is believed that philodendron flowers do not have much decorative value.
Philodendron flowers are collected in a spadix, covered with a single spathe. Unfortunately, philodendrons very rarely bloom indoors. Buds appear only in ideal conditions, combining space, warmth and high humidity. Flowering can only be expected from philodendrons growing in greenhouses or winter gardens.
Diseases
In winter, stems and roots can rot if exposed to excess moisture and low temperatures.
Philodendron most often suffers from stem and root rot. Typically, this fungal infection appears in winter when there is excess moisture and low temperature.
At the first signs of disease, you should limit watering, increase the temperature, and sometimes transplant the flower to another soil.
Sometimes pests of indoor plants settle on the flower: thrips, red spider mites and scale insects. In the fight against them, you should not use traditional methods. With their help it is impossible to destroy all insects. Only insecticidal preparations can save the plant.
A fungal disease can affect a flower even in the warm season. It should be remembered that philodendron does not tolerate stagnation of moisture in the soil. The onset of decay is usually accompanied by yellowing and wilting of the leaves . Therefore, if there are any signs of fungal infection, drainage should be checked and watering adjusted.
In case of severe root rot, it is necessary to wash the roots of the flower and remove the diseased parts, and sprinkle the sections with activated carbon. After this, the plant is transplanted into new soil.
Difficulties in growing
Despite the unpretentiousness of the tropical forest dweller, problems can arise if care is taken incorrectly.
- A decrease in the size of new leaves, an increase in internodes, and loss of color of the leaf blade are signs of a lack of lighting.
- Yellowing of leaves can be caused by overwatering.
- The leaves turn brown and fall off - the plant lacks moisture.
- When the soil is wet, the leaves lose their elasticity. The reason is either rotting of the root system due to overwatering, or too bright light.
- The appearance of black spots on leaves, including between the veins, is usually a consequence of exposure to low temperatures.
- Brown spots are sunburn.
- The leaves turn brown, the tips lift up due to the dry air in the room.
- Wrinkling of leaves and the appearance of chlorotic spots are a consequence of treating the flower with chemicals.
- The leaves have turned pale - probably the flower does not have enough fertilizer or the acidity of the soil is not suitable.
Brown spots on philodendron leaves.
Philodendron diseases
The plant is most often affected by stem rot. It appears due to excessive watering and leads to soft tissues and loss of turgor by the plant. If the philodendron is not severely affected, you can try to save the plant by re-rooting. The trunk is cut off a few centimeters above the rotting site and rooted in soil or water.
Pests
Philodendron is affected by pests due to improper care, which weakens the plant. It is usually attacked by spider mites, aphids, thrips, and scale insects.
- Spider mites suck the sap from the plant, which causes yellow spots to appear on the leaves. In the affected areas, if you hold the sheet up to the light, puncture points are visible. On the reverse side there is white husk-dandruff - the skins of pests. For prevention, high humidity in the room should be maintained. And if the tick is already infested, acaricidal drugs are used.
- Aphid colonies on shoots are visible to the naked eye. First, the top of the plant becomes deformed, then the leaves curl, sweet dew appears, where sooty fungus later develops. To combat aphids, wash the plant with soapy water. If the damage is severe, use chemicals - Fitoverm, Intavir or others.
- Thrips leaves noticeable marks on the leaves in the form of silvery streaks and spots. The affected areas are strewn with small black dots - the excrement of the pest.
- When attacked by scale insects, brown or translucent plaques are noticeable on both sides of the leaf, representing nothing more than the shell of the pest.
Thrips and scale insects are fought in the same way. First, the affected plants are washed with a soap solution, then the soil is spilled with a systemic insecticide such as Aktary or Confidora. Repeated soil treatment is carried out after a week.
Problems
Philodendron cannot be called a capricious plant, but sometimes even experienced gardeners grow poorly. The reason for this is some mistakes in caring for it.
Often the leaves of this plant turn yellow . This can happen for various reasons. If yellowness appears along the edges of the leaves, the plant is watered too much. If yellowing soon spreads to the entire leaf blade, it is due to a lack of fertilizer.
Excess sunlight causes yellow, dry areas on the leaves - burns.
If the plant suffers from insufficient lighting, the leaves decrease in size, the shoots become elongated, and the distance between the leaves increases. With a large lack of light, the plant may have whole leaf blades instead of dissected leaves; in variegated varieties the leaves turn green.
Varieties and varieties
Compact culture - Philodendron Birkin (Philodendron hybr. Birkin) - obtained artificially. The rare plant became the basis for the development of new varieties of the Silver series: Silver Queen and Silver Dust.
Silver Queen
Silver Dust
These indoor crops are similar to their predecessor in the shape of their leaf blades. However, their bright green crown has a beautiful silver tint.
Reproduction
In indoor conditions, philodendron is propagated vegetatively. To propagate philodendron, apical and stem cuttings are used. In some species it is possible to root a separate leaf with a heel.
Cuttings are cut in March or early April . They can be rooted in water or used as a substrate - wet moss. The cuttings are buried in the moss, and a plastic film is stretched on top. It is needed to maintain the required humidity.
You can root cuttings in a greenhouse. They are transplanted into separate pots only when they grow confidently.
A new plant can be obtained from a part of the stem with aerial roots . The stem at the site of root formation is wrapped with a film of wet moss. The moss is periodically moistened until a real root system is formed from the aerial roots. Then the trunk is cut below the root, and the plant along with the moss is planted in a pot with soil mixture.
You can read more about plant propagation methods here.
How to propagate philodendron
Several methods are used for its propagation: aerial roots, cuttings, seeds. Work is carried out in the spring.
The simplest and easiest way is to root aerial roots. It is suitable for climbing philodendron. The selected piece of shoot is placed on a damp substrate of peat or sphagnum moss, and slightly buried in the ground. It takes root within a month. It is then separated from the mother shoot. The plant is ready for a new life.
A common method is propagation by cuttings and leaves. First, a shoot with 2-3 leaves is selected. A sharp knife is used to cut it. The shoot should dry out within a few hours. Then do this:
- Prepared small pots are filled with soil consisting of peat and sand in a 1:1 ratio. Moisturize it.
- Lay the cuttings on top and press down lightly. It is important to ensure that the growth point is not covered.
- Create greenhouse conditions. That is, they cover it with a cap made of plastic film, a cut bottle, or glass. The temperature required for germination is 25-30°C.
- Periodically, the greenhouse is opened for ventilation and moisture, if the need arises.
Germination of cuttings
After about a month, the greenhouse is opened. After the cuttings have rooted and two new leaves appear, they are transplanted into a large container. In the future, care is the same as for an adult philodendron.
The same method is used when rooting leaves. However, you should pay attention to the presence of aerial roots or a piece of heel.
Pruning cuttings has a positive effect on the development of philodendron. It rejuvenates, new shoots grow.
Tree-like plants reproduce by seeds. It's easier to buy them in a specialized store. Pay attention to the expiration date indicated on the packaging. Stages of work:
- You should start by soaking the seeds for 8-12 hours. It is better to use distilled water.
- Sow the seeds in soil prepared from peat and sand. Do not sprinkle the seeds; let them lie on the surface. Water carefully from a spray bottle.
- Create greenhouse conditions, install in a lighted place, but not in the sun. Ventilate periodically.
- Fully open the shelter (but gradually, not immediately) after 2-3 leaves appear. This usually occurs within 2 to 7 weeks.
- After 2.5 months, plant each seedling in a separate small pot.
The method is quite labor-intensive. At home, the desired outcome is not always achieved.
For tree-like species, there is another way of reproduction - by fragments of the trunk. An incision is made on the stem near the top and sprinkled with root. Then moistened moss is applied to this place, wrapped in cellophane film, and tied.
A prerequisite is the tightness of the shelter and the moist state of the moss. You can check and wet it occasionally.
The appearance of roots visible through the shelter is a signal to open it, cut off the top and plant it in a pot. The cut area on the stem is sprinkled with activated carbon powder. Soon new shoots will grow there.
Transfer
Young philodendrons need to be transplanted into new soil annually. This is done in the spring in April or early May.
After 5 years of age, philodendrons can be replanted once every 2-3 years . If the plant becomes so large that it will be impossible to replant it, you need to replace the top layer of soil with fresh fertile soil mixture twice a year.
In this case, the land is replaced in April and September.
For replanting, you should not take a pot that is too spacious, since the soil, which is not occupied by roots, quickly turns sour and becomes a breeding ground for fungal infections. But a pot that is too small is also harmful - in it the leaves of the flower will dry out and fall off. The size of the pot should be 2-3 cm larger than the previous one.
A healthy plant is replanted using the transshipment method. In this case, its roots suffer least from this procedure, and the transplanted vine quickly takes root in the new soil and begins to grow. Plants with root diseases require revision of the root system and complete replacement of the old soil with a new substrate.
Philodendron ivy at home
Caring for philadendron at home is quite simple. This is a very strong plant that can take a wide range of conditions. Experienced gardeners recommend regularly pinching the houseplant so that the ivy-shaped philodendron grows lushly. Otherwise, the stems grow too long, making the plant unattractive. Try to pinch the plant closer to the internode, because the bare trunk will simply die, and a new shoot will grow from the internode. Use sharp scissors or pruning shears.
Watering
During active growth, water sparingly, giving the plant enough moisture each time you water. Be sure to let the top layer of the substrate dry out between waterings. During the dormant period, such an amount of moisture is added to the substrate that will protect the soil from completely drying out.
Philodendron ivy tolerates dry indoor air well, but humid air is guaranteed to produce larger leaves and faster growth. It is advisable to increase the humidity in the room by spraying the indoor plant regularly, not only in summer, but also in winter. It is best to use purified water; minerals found in tap water will accumulate on the leaves.
Lighting
The plant can withstand low light for quite a long time. Although, like most shade-tolerant plants, it will be better if you place the pot in a bright sunny place without direct sunlight (diffused light).
Temperature
Philodendron hederaceum will grow well at normal room temperatures of 15-22ºC, but will not tolerate temperatures below about 13ºC.
Fertilizer
During the growing season, while the flower is actively growing, standard liquid fertilizer should be applied once every 2 weeks.
philadendron care at home with photos
Transfer
Like most houseplants, philodendrons need to be repotted into larger containers once the plant's root system has filled the pot. You can replant at any time of the year, except for a short rest period. Use a container or pot with drainage holes to prevent root rot.
The choice of soil can be approached simply, since the plant is unpretentious and feels great in a mixture that is quite loose and well-permeable to air and water (high humus content), for example, peat, humus and leaf soil and add a little sand.
Reproduction
Philodendron cuttings using stem and apical cuttings, seeds are widespread, and crossing methods are also quite popular among avid gardeners if there are several flowering plants. Try propagating the plant during the growing season. Along the branches there are small brown tubercles-buds. Roots will grow from the buds upon contact with soil or water.
philadendron care at home photo
There are many ways to propagate this plant, the easiest way is to take a large stalk and place it in water with a few pieces of horticultural charcoal to reduce the chance of rotting. When young roots appear, transplant the cuttings into a pot. The plant can also propagate within its own pot by securing the sprout from the root system into the substrate using wire. In contact with the soil, new roots will sprout on the sprout in the very near future.
Bloom
The plant blooms quite rarely when grown in cultivation. In its natural conditions, during the flowering period, the plant modifies one of its leaves, which turns into a hood-shaped blanket. Inside the hood the spadix (flower) is born. The inflorescence contains reproductive particles which, once ripe, can be pollinated and on the female spadix small tiny flowers can then be seen under a magnifying glass.
Diseases
Possible damage from aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs. Root rot can occur in overly wet soils. If the plant has small leaves or long gaps between the leaves, this indicates that the flower is not receiving enough light. To correct the situation, place the plant in a bright place, but not in direct sun.
Toxicity
Parts of the plant are known to contain calcium oxalate crystals in varying concentrations. Although the plant is known to be toxic to mice and rats, current literature also reports toxicity to cats. The possible toxic effects of the plant on humans are currently unknown.
Application
Philodendrons are known to many for their ability to thrive in the low light conditions found in many homes and offices. The plant can be grown as a hanging plant or as a potted houseplant using supports or in hanging baskets.
In tropical and humid subtropics, Philodendron hederaceum can be used as a ground cover plant. In summer cottages, the flower can be used for vertical gardening on gazebos and trellises, giving the landscape design a tropical look; the plant will look especially impressive around patios, window sills and pools.
Philodendron hederaceum is also noted as one of the best houseplant species for removing formaldehyde, especially high concentrations. It is capable of absorbing 80 to 90% of the formaldehyde currently used in water-based paints, roofing felt or insulation materials, adhesives in carpeting and even laminated wood floors!
a brief description of
- The foliage is green.
- Cultivation – potted, climbing, container.
- Height: 3-6 meters
Proper care
- Watering (rest period) - moderately.
- Watering (growing season) is minimal.
- Lighting – diffused bright light.
- Temperature (rest period) - minimum 13 ° C maximum 24 ° C.
- Temperature (growth period) - minimum 13 ° C maximum 24 ° C.
- Air humidity is low.
Philodendron is a plant that quickly gets used to poor atmospheric conditions. It tolerates drafts, gas combustion products, and smoke very well.
PS Interesting for the population of rural areas is the fact of the existence of the TOPAS cleaning system. This system has a whole list of properties that deserve attention, and it can also be easily installed independently. The price of TOPAS will pleasantly surprise and delight you.
Description of the plant and species
Philodendrons are native to the tropical forests of Central and South America. There are many varieties of these plants, differing in appearance and leaf shape. Among them are climbing vines, tree-like plants and stemless rosette herbaceous varieties.
About a dozen species of philodendrons are common in indoor culture. Almost all of them are vines. Indoor philodendrons have long flexible shoots and aerial roots that help them climb up the supports.
Philodendron leaves vary in size, shape and color of the leaf blade.
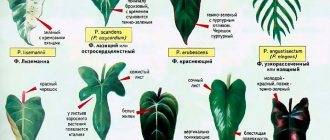
The most common species in indoor culture:
- Philodendron graceful;
- Philodendron climbing;
- Philodendron blushing;
- Philodendron Sello.
Philodendron graceful is a large, tall vine with a thick, unbranched trunk. Its leaves reach a length of 70 cm, rounded and strongly dissected. Suitable for landscaping large spaces.
Philodendron climbing is a vine characterized by rapid growth. It has small heart-shaped leaves of a light green hue. The stem of the plant is long, unbranched. There are varieties with variegated leaves.
Philodendron blushing is a very decorative evergreen vine. It has large shiny arrow-shaped leaves. The stem of the plant has a red-green hue. Grown as an ampelous plant.
Philodendron Sello is a vine with a thick woody trunk, the shoots of which grow up to 1.5 m long. Its leaves are very large, up to 90 cm in length, oval, deeply indented.
Philodendron care
Temperature: In summer, normal room temperature. In winter, with shorter daylight hours, it is desirable to keep it cooler, at 18-22°C, but not lower than 15°C. Avoid cold drafts. If there is no direct flow of warm air from the batteries, then philodendrons overwinter well at normal room temperatures of 22-26°C, provided they are provided with additional lighting (using fluorescent lamps).
Lighting: A bright place, with protection from direct sunlight at midday, very light partial shade. Variegated forms require a little more light, preferably morning or evening sun. The climbing philodendron has more delicate leaves than other species; it is only suitable for an eastern or northwestern window sill, or placement under shade. Philodendrons are unpretentious plants, many of them grow in completely artificial light and next to a north window. But truly powerful and spreading bushes form only in good light. My philodendron radiata grows from May to October on a southern windowsill, the only shading is a light mosquito net.
Watering: Moderate in spring and summer, the soil should be moist all the time (not too damp), this means that by the next watering the soil in the upper third of the pot should dry out well. In winter, watering is reduced, just not allowing the soil to dry out completely; the soil should dry out in the upper half of the pot, then you need to wait another 3-4 days before watering. If there is excess watering, the lower leaves may turn yellow; if the soil dries out for too long, cakes, is too dense and does not allow the roots to breathe, root rot may develop. Don't forget that philodendrons are mostly epiphytes, which means the roots need to breathe, which doesn't happen in dense, waterlogged soil. If there is not enough moisture, the tips of the leaves dry out, and if it is too dry, the entire lower leaves, as a rule, dry out and fall off. Sometimes, with excessive watering, droplets of water appear on the petioles and leaves.
Fertilizer: From March to October, philodendrons are fed with complex fertilizer for decorative foliage plants. Feed every two weeks. For large tree-like vines, once a summer, well-rotted compost can be added to the top layer of soil during replanting, or without it. When feeding philodendron with fertilizers, it is important not to overfeed, otherwise the tips of the leaves turn yellow or brown, and the leaves themselves wither and become lifeless. If you have added a significant proportion of humus to the soil, then do not feed it with other fertilizers for at least 2 months. On the contrary, quite often philodendrons suffer from a lack of nutrients in the soil if they are not replanted for a long time and forget to feed them. At the same time, the leaves become smaller, their tips dry out and turn yellow, and the plant lags behind in growth.
Air humidity: Philodendrons are inhabitants of moist forests or floodplains; they love moist air. Unfortunately, dry air cannot be compensated for by excessive watering. It is necessary to regularly spray the plants in spring and summer, and in winter, if it is better to place trays with wet sphagnum moss near the heating system, hang the radiators with a wet sheet. Small plants are given a shower several times during the summer to wash away dust. For large plants, the leaves are regularly wiped with a damp sponge.
Care Tips
- Temperature: Moderate, about 18-20°C in summer, not lower than 15°C in winter. Avoid cold drafts.
- Lighting: A bright place, with protection from direct sunlight, light partial shade. Variegated forms require a little more light, but also in a semi-shaded place. Climbing Philodendron can grow in more shaded areas.
- Watering : Moderate in spring and summer, the soil should be moist all the time. In winter, watering is reduced, but the soil is not allowed to dry out; at this time the soil is only slightly moist. If there is too much watering, the lower leaves may turn yellow; if there is not enough watering, the tips of the leaves dry out.
- Fertilizer: From March to October, philodendrons are fed with a complex fertilizer for indoor plants. Feed every two weeks. For large tree-like vines, humus can be added to the top layer of soil once a summer during replanting or without it.
- Air humidity: Philodendrons need to be sprayed regularly in spring and summer, as well as in winter if there is a heating system nearby. Small plants are given a shower several times during the summer. For large plants, regularly wipe the leaves from dust with a damp sponge.
- Transplantation: Every year in the spring, young plants and three to four years later - old ones. Soil: 2-3 parts turf, 1 part peat soil, 1 part humus, 0.5 parts sand. When large specimens are grown in too small a pot, spots appear on the leaves, they turn yellow, and the plants are stunted.
- Reproduction: By apical or stem cuttings. For rooting, it is better to use soil heating and covering with film. Large vines can be propagated by a leaf cut with a heel.
Popular varieties of philodendrons - table
| Name | Appearance of the plant | |
| Climbing (acute-leaved, clinging, creeping) | Size up to 2 m. Shoots are thin and flexible. The leaves are dense and shiny, heart-shaped, entire. Length - up to 15 cm, width - 8 cm. Color - dark green. Young leaves have a bronze tint. | |
| Blushing | Height - up to 1.8 m. Shoots are fragile and thin. The trunk becomes woody with age. The inflorescence is white. The leaf shape is elongated, pointed at the end. The petioles are long, dark red at the base. Leaf length is up to 30 cm, width - up to 25 cm. The outer side of the leaf plate is painted green, glossy. The inner one has a reddish tint. | |
| Atom | The plant is compact, with an erect stem. The leaf shape is very decorative - five-lobed, with wavy edges. The leaf plates are painted bright green, glossy. Length - up to 30 cm. | |
| Guitar-shaped | An evergreen vine up to 2 m high. The young leaf is shaped like an elongated heart. An adult is deep-lobed, resembling a guitar, up to 30 cm long. | |
| Radiant | The plant is fast-growing and unpretentious, of medium size. The leaf is up to 20 cm long, medium hard, heavily dissected. | |
| Spear-shaped (domestic) | Fast growing liana. The leaf is spear-shaped, up to 45 cm long, glossy. Green color. With age, the leaf blades become more cut and wavy. | |
| Cobra | Creeping vine. The leaf is dark green with light spots. The shape is elongated, with a sharp tip. Leaf length is up to 14 cm, when grown vertically - up to 25 cm. | |
| Sello | The trunk is smooth, woody, up to 3 m high. Traces of fallen leaves are visible on the trunk. The leaves are triangular-heart-shaped, deeply double pinnately dissected. There are 10 or more narrow-lanceolate lobes on the leaf. The length of the leaf plate is up to 90 cm. | |
| Xanadu | In room conditions it reaches 1.5 m. Young leaves are soft, slightly separated. Over time, they become rigid and grow up to 40 cm in length. They become heavily feathered. | |
| Lobed | Evergreen, climbing liana. Branches of medium thickness, flexible. The leaves are dark green, leathery. The shape is ovoid, turning into three times dissected. Subsequently it can be divided into 5 shares. The petioles are long and approximately equal to the length of the leaf - up to 40 cm. | |
| Golden black | Climbing liana. The leaves are bronze-green and velvety. The top is covered with golden veins, the underside is reddish. The leaves are oblong-lance-shaped, drooping, up to 80 cm long. | |