If previously only experienced gardeners were engaged in breeding orchids, over the past few years the number of fans of these flowers has increased sharply. The high demand for them is explained by the wide variety of varieties and the beauty of the buds. However, growing such a plant is not easy: humidity and proper lighting for orchids are extremely important growth conditions.
Description and main characteristics of the device
There are many different lamps for lighting a flower. How to choose the right orchid?
Energy saving lamps (CFL)
- Their advantages over conventional incandescent lamps are obvious: They consume 4-5 times less energy. And the return is higher;
- Long warranty periods;
- Security is higher. Short circuits are very rare.
- Blue;
- Only 20% of the heat energy is spent on heat;
- MaxGrow;
Orchid lamps should not get hot.
Please note:
- The base size can be standard E27. and smaller – E14;
- Warm colors (closer to yellow) - below 4000 K. During flowering;
- Daylight – 4000-6440K. Universal;
- Cold tones (close to blue) – more than 6500 K. During the growing season.
Luminescent
- Gases (often mercury), thanks to the coating of lamps with phosphor, provide the presence of ultraviolet rays: LB (white color);
- LD (daytime color);
- LDC (daytime color with improved color rendering).
- Philips;
- T8 (diameter 26 mm);
Halogen
- Metal halide devices are also called gas discharge devices. These are almost the same as incandescent lamps for plants. But improved and more expensive;
- Their shapes and color spectrum are varied. But for plants (and orchids), purchase special models;
Many amateur gardeners use lighting for orchids.
- White and blue models: Sunmaster Leuchtmittel Wuchs 600 W;
- Greenbud MH: 250 W;
- 400 W;
- 600 W.
Mercury gas discharge
- The principle of their operation is the same as that of fluorescent ones;
- But the marking is different;
Mercury gas discharges operate on the same principle as fluorescent ones.
- You need a glow temperature from 3,200 to 4,200 K;
- There are also sodium gas discharge lamps. Low and high pressure.
LED
- LED lamps are in greatest demand among orchid lovers;
- What attracts: Cost-effectiveness;
- Long service life;
- Environmental Safety;
- Resistance to temperatures, mechanical stress;
- No UV radiation.
LED phytolamps.
Of all types, experts consider the following lamps to be the most effective for orchids:
- For flowering: Sylvania 250 W, HPS-TS 400W;
- Osram Nav-N 250W, 400W, 600 W, 1000 W;
- Philips Son T-plus 400 W, 600 W;
- Greenbud HPS 400 W, 600 W, 1000 W;
- GIB Lighting Flower Specter HPS 250 W, 400 W,600 W.
- Sylvania Growlux 400W, 600W;
LED strips
Now on Aliexpress you can order a 1 meter long LED strip with different combinations of blue and red LEDs for a few dollars. To remove heat, it can be glued to an aluminum threshold for linoleum joints. You will also need a 12 Volt power supply, which it is advisable to order with a current reserve of at least 0.4A.
For some reason, the “flimsy” 100 mA power supplies offered by the seller stopped working after 2-3 weeks of use, after that I ordered a 0.4A power supply (it’s already so solid in the form of a rectangular box, like a laptop charger), I think it works with it there won't be any problems.
Calculation of drivers and choice of basis
Linear LED Driver
The power supply is an essential part of the lamp. It equalizes the output voltage and supplies the LEDs with optimal power.
The documentation for the tape indicates the value of the voltage drop at different current levels. This value must be multiplied by the number of diodes. The optimal number of drivers is selected from the resulting parameter.
Recommendations to help with installation and connection:
- The best driver option is 50 W. More powerful devices will heat up and cost more. In terms of current, the optimal choice of source is 600 mA.
- During driver calculations, the actual power of the LEDs should be taken into account, not the maximum power. It is calculated as the current of the source used multiplied by the voltage drop.
When choosing a driver, you need to pay special attention. Without this element, normal operation of the phytolamp is impossible.
Any material can be used as the surface of the lamp. Phytolamps are often made from plywood or boards, but in this case it is necessary to consider a cooling system. It is better to take aluminum - then the heat will be removed from the surface and the device will last longer.
How to measure light
You can measure the light with a lux meter. Some measure light in footcandles, others in lux or klx. You can also use a 35mm camera to measure the light. Here's how to do it: • Set your camera to 25 ASA. • Set the shutter speed to 1/60th of a second. • Place a white sheet of paper in the area where the plant leaves will be located. • Focus on a white piece of paper from 1 foot away. • Record the aperture reading in the viewfinder. Here are the approximate footcandles corresponding to different apertures: f/2 = 100 f/2.8 = 200 f/4 = 375 f/5.6 = 750 f/8 = 1500 f/11 = 2800 f/16 = 5000 Remember, maximum light should be at noon on a bright summer day.
Lamp installation options
There are several ways to mount lighting fixtures:
- Table lamp for orchids or lamp. This option should be used in cases where the orchid pot is on a windowsill, shelf or table. To speed up the process of photosynthesis, it is worth installing a separate small lamp above each plant. In this case, you need to ensure that the main flow of light is directed not at the buds, but at the leaves.
- Pendant lamps. If one light source will be used for several pots, then it is better to mount it a little higher. An example is a design in which the lamp is mounted on a horizontal crossbar or on a vertical stand.
- Fastening to furniture. You can choose this method in cases where pots with orchids (and other plants) are installed on shelves. Then the top shelf will become a good platform for mounting lamps that illuminate the lower tier.
Choosing a pot for growing orchids
It's no secret that orchids are sold in transparent pots in stores. This container is the best choice for the plant. Planting a flower in a ceramic or clay pot is not the best solution. The plant may die due to rotting of the roots, since you will not be able to correctly assess the condition of the root system. Under natural conditions, orchids grow on trees. It actively uses its roots for photosynthesis. With their help, it is replenished with moisture during tropical downpours.
The roots should not be deprived of light. Therefore, the ideal container for planting a flower is a transparent plastic pot. It is necessary to make slits on the walls and bottom of the vessel so that the root system is freely ventilated. Currently, specialized stores sell containers for orchids with ready-made holes. These pots are ideal for planting. Sometimes boxes made from twigs are used for plants. For planting it is necessary to use drainage. You can use perlite or small crushed stone. Drainage should occupy no more than 1/3 of the pot.
Conditions where it is better to grow or choosing a place on the window
When choosing where to place the orchid in the house, you need to take into account the orientation of the windows. South-facing window sills are ideal for winter placement. The epiphyte develops well and produces flower stalks even without additional lighting.
However, in summer, shading is required here so that the leaves do not get burned due to intense exposure to sunlight. When placed on the north side, the orchid will need artificial lighting in winter. It is recommended to install pots with shade-loving varieties of orchids on western-oriented windows.
The optimal place for light-loving varieties is eastern window sills.
Their location prevents the occurrence of burns in the morning. In winter, on the eastern side, the sun's rays do not linger for long, so artificial lighting will be required.
Effect of light on plants
Light is the main source of energy necessary for the formation of hydrocarbons, fats and proteins that make up plant cells. It is absorbed by the green pigment of leaves, chlorophyll, and participates in the formation of organic substances along with water, carbon dioxide and trace elements. The combination of intensity and duration of solar insolation under natural conditions determines the change in phases of plant life - active growth, development of shoots and leaves, formation of buds, flowering, dormancy.
It is difficult for indoor plants to provide the required level of illumination for the following reasons:
- Light penetrates through a limited surface of window glass, so its intensity drops sharply at a distance from the windows.
- Window sills are often exposed to diffuse rather than direct sunlight.
- Windows on the lower floors of buildings are often obscured by nearby structures and trees.
- In rooms with dark wall surfaces and furniture colors, a significant amount of rays are absorbed by furnishings.
- When windows face north, northeast and northwest, less sunlight enters the rooms compared to south, east and west.
The upper floors of buildings and southern windows experience higher solar insolation, so flowers standing on window sills in the summer can get leaf burns and overheat.
It is better to place succulents on southern windows in summer. To protect the roots from overheating, you can place the pots in additional containers with sand or fine expanded clay.
How does changing the direction of light affect
Some flowers react to changes in the position of the bush in relation to the light source by dropping buds and flowers, for example, geranium, gardenia, fuchsia, and zygocactus. During the flowering period, it is not advisable to move them from place to place. In many species, shoots on the side of the light source grow denser and longer. For uniform development of decorative leafy plants, it is recommended to periodically rotate them along their axis by several degrees.
Effect of day length on flowering
The length of daylight hours has a significant impact on the flowering and fruiting of many crops. In a temperate climate zone, its shortest duration is 8 hours, maximum – 16 hours.
Based on the ratio of daylight hours and the onset of flowering, they are divided into:
- Species that require lighting for significant periods of time during the day. These include Saintpaulia, hydrangea, cineraria, gloxinia, calceolaria and some other flowers. Given sufficient daylight and good conditions, they grow and develop throughout the year. If these plants receive only natural light, they form and open buds from early spring to late summer.
- Species that bloom during short daylight hours (8 to 10 hours). These are plants such as zygocactus, poinsettia, chrysanthemum, azalea, and Kalanchoe Blossfeld.
- Indoor flowers that form buds at any length of daylight. These include evergreen begonia, rose, abutilon and some others.
- Plants that bloom when long daylight hours are replaced by short ones or vice versa. Thus, cyclamen and camellia bloom in winter, and grandiflora pelargonium blooms in spring.
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a complex biological process involving the production of carbohydrates from inorganic substances under the influence of solar energy. By absorbing carbon dioxide and water, the plant synthesizes organic substances and releases a byproduct of photosynthesis - oxygen.
These processes occur predominantly in leaves containing chloroplasts. Carbon dioxide penetrates inside orchids not only through the green mass, but also through the flowers and stems. The root system also participates in photosynthesis, so transparent containers are preferred for growing plants.
Basic rules for caring for flowers at home
First of all, it should be remembered that the homeland of most orchids are countries with a uniformly warm climate, the temperature in which is not subject to significant fluctuations and always remains at a fairly high level. Also, do not forget about humidity and the length of daylight, which, as a rule, is at least 12 hours.
Knowing this, we can highlight the basic rules for caring for orchids:
- Flowers do not like it when they are too cold or too hot; the temperature in the room should be stable, but not exceed 30 degrees and not fall below 10.
- Plants need to be provided with high humidity, otherwise there is a risk that they will begin to dry out.
- Orchid roots need access to air, so the soil should not be dense, preferably, of course, special soil, selected depending on the specific type of plant.
- Periods of abundant watering must be alternated with periods of complete drying, as usually occurs in the natural habitat.
- All orchids need intense lighting; without it they will never actively grow and bloom. This condition is the most difficult to comply with, especially in winter.
Read more about the optimal conditions for keeping orchids in our material.
Mistakes when organizing orchid lighting
Common mistakes:
- Wrong choice of lamp light spectrum.
With an abundance of red rays, the orchid will bloom profusely, but the peduncle will be thin and can be easily damaged.
Under the influence of blue spectrum rays, the flower will grow strong and strong, but you may not wait for flowering.
- Too much light.
Excessively long daylight hours are not good for the orchid. In summer the plant can cope with the load, but in winter it may wither.
- Insufficiently intense light.
The orchid will be lethargic, the leaves will darken and take on a bluish tint. This is how a lack of ultraviolet radiation manifests itself.
Why are phytolamps needed?
All plants need light to live - this is the main source of their energy. Chlorophyll is a green pigment in leaves and shoots that absorbs light rays, thereby triggering the process of formation of nutrients and other necessary compounds - photosynthesis (you can find out how to properly organize the necessary conditions for photosynthesis for an orchid here).
There are two types of chlorophyll:
- Chlorophyll A, which absorbs the blue part of the light spectrum.
- Chlorophyll B, which absorbs the red part of the light spectrum.
Important! For the harmonious growth and development of indoor orchids, it is necessary that both types of chlorophyll (A and B) be intensively involved. The main problem is that in natural light, blue waves can be absorbed throughout almost the entire day, while red waves can only be absorbed in the morning and evening
But, in the winter season or in the absence of sufficient lighting in the room, the plants will lack both the former and the latter.
The main problem is that in natural light, blue waves can be absorbed throughout almost the entire day, while red waves can only be absorbed in the morning and evening. But, in the winter season or in the absence of sufficient lighting in the room, the plants will lack both the former and the latter.
In order to compensate for the lack of daylight, there are special phytolamps for floriculture. You can choose either a universal option, in which a special ratio of blue and red light is pre-combined, or individual lamps, supplementing them with regular white light if necessary.
Types of lamps by light spectrum
- Bicolor.
Red (660 nm) and blue (450 nm) colors of the spectrum are mixed. An option favorable for mature plants that are illuminated mainly by natural light.
- Multispectral.
A combination of red, blue and warm white colors provides suitable lighting for plants with dense foliage and flowering plants.
- Full spectrum (Full Spectrum).
Suitable for growing plants without sunlight. The only negative is that the lamps irritate the eyes and are recommended for installation in non-residential premises.
To compensate for the adverse effects on vision, Fullx2 models are available. They feature the addition of white light, but are more expensive than Full Spectrum bulbs. These lamps are recommended for illuminating plants in living rooms.
Disadvantages of phytolamps :
- unpleasant glow for the eyes;
- high price;
- short service life - only 1 year.
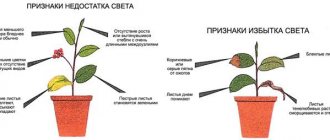
Signs of too little or too much light
The ability of indoor flowers to adapt to light levels varies. There are light-loving, shade-tolerant and light-indifferent plants. Insufficient lighting has an adverse effect on plant development. Sensitivity to a decrease in its intensity is higher in light-loving species.
The lack of light is indicated by the following changes in the appearance and development of indoor flowers:
- Plants with light or variegated leaves change color due to an increase in the amount of chlorophyll to better absorb incoming light. They acquire a dark green color, sometimes become narrower and slightly elongated.
- The stems stretch in the direction of the light, but grow thin and weak. The length of the internodes increases, and at the same time their fragility increases.
- After some time, the growth of shoots and leaves stops due to deterioration of photosynthesis and lack of organic matter.
- Some plant species do not bud or bloom for a long time.
With excess light, the following changes are noticeable in the appearance of the bushes:
- The leaves turn yellow-green due to the partial destruction of chlorophyll. They can also lose turgor, drooping down, and in some cases dry out due to loss of moisture. When burned by the bright rays of the sun, the leaf plates acquire a bronze tint.
- The growth rate of stems decreases, the distance between nodes decreases, the width increases and the length of leaves decreases.
↑ How to enhance lighting yourself
The simplest and cheapest way to enhance natural light is to cover the walls and the window sill itself with foil. This shiny material reflects heat and light well. You just need to take into account that foil is effective only in sunlight. If the day is rainy or cloudy, the foil will not provide reflection.
Foil has several advantages when used as a reflector:
- the level of solar illumination increases by 20-30%;
- heat and light are distributed evenly across all plants in the container. Usually the corners of the window sill are poorly illuminated by lamps, but with foil there is no such problem;
- the appearance of seedlings occurs evenly, the shoots grow evenly, without bending the stem.
To arrange such lighting you will need foil, masking tape and scissors. The foil is evenly distributed over the window sill and its walls, secured with tape.
Which UV bulbs can you choose for growing flowers?
LED
This is the most effective type of lighting.
They have high power with low consumption, they have low heating and a long service life.
The best option for indoor plants is the multispectral option. Several additional spectra have been added to such devices, which significantly affect the flowering of many indoor plants, including fastidious orchids.
Luminescent
Another type is luminescent. They are distinguished by uniform illumination along the entire length and the ability to adjust the brightness of the glow.
However, such lamps contain toxic mercury vapor inside. And for the system to operate, a special ballast mechanism will be required.
Sodium
If you cannot tolerate specific bright purple light, you should pay attention to sodium phytolamps. They emit a warm yellow glow, so they would be appropriate in a living room
They have high power (even one may be enough), are economical and last a long time.
There are also disadvantages:
- They get very hot and can explode if water gets on the surface of the flask.
- They also require a ballast, which increases the already considerable costs.
Tips for choosing
In order to select a functional and reliable device to support the development of indoor and greenhouse crops, you need to take into account certain nuances
- The selection of a phytolamp should begin by calculating the area with which the device will work. It is also worth deciding on the frequency of lighting. A clear understanding of the requirements for the device will greatly facilitate its selection. As a rule, manufacturers indicate on their products information about the power of the product and the recommended operating area.
- Before purchasing, you should also decide at what distance the device will be placed relative to the plants. The best option would be to purchase phytolamps with the ability to regulate their location and height.
- Before purchasing lighting devices, it is also worth sorting existing crops based on the growing season.
- For small spaces, such as, for example, a window sill, you can opt for models with medium emitted power. As practice shows, indoor flowers will need fluorescent lamps with a glow temperature of about 6500 K. For greenhouses and conservatories in winter, high-performance and large lamps of a universal spectrum will be needed.
- To equip a room with lighting, you should give preference to one type of lighting fixture in order to create the most comfortable conditions for crop growth.
Power and types of backlight lamps
What light is suitable for orchids at home? Our scientists and specialists calculated the required amount of light, its intensity and duration:
- Lighting means should not be heating. The total power of fluorescent lamps is 100-120 W. And there is no need to determine the lighting power “by eye”. After all, there is a marking on the lamp;
- It is difficult to find consensus between lamp distance and luminous efficiency for numerous orchid species. But you must do it. Even with your hand you should not feel the heat at a distance of 10 cm from the lamp.
Important! Here is an example of the lighting power of two 40 W fluorescent lamps in a lamp with a reflector:
- 7000 lux – distance from the plant 5 cm;
- 5200 lux – 10 cm;
- 3000 lux – 20 cm;
- 1700 lux – 50 cm.
This helps to decide on the means of illuminating the orchids. But few people do the calculations:
- Both beginners and experienced gardeners try to purchase fluorescent or LED lamps;
- They do not recommend using a regular energy-saving lamp. The only exception is if you have several orchids;
- Special phytolamps are in particular demand. If you have a solid collection, the lighting itself should match it.
Phytolamps provide the orchid with ultraviolet rays.
Distance from lamp to orchid
The lamps should be at a distance of 30-50 cm from the orchid leaves.
The optimal distance is:
- 30 cm from the leaves of the plant to the lamp for light-loving plants;
- shade-loving lamps .
It all depends on the power of the lamp itself.
A lamp that is bright for our eyes may be weak for an orchid. And the weak one for our perception is the most suitable for an orchid.
Important! the incidence of rays from the side as the approach of night, and the processes of morphogenesis, which are responsible for preparing the flower for the dark time of day, are activated.
How to tell if your plants are getting enough light
The appearance of indoor flora serves as a reliable indicator of whether it has enough light. The reasons for poor growth may have other origins, but it is worth thinking about the lack of lighting if the following signs are observed in flowers:
- Leaves grow to a smaller than normal size.
- The color of leaves and stems becomes less saturated.
- The distance between two adjacent nodes (leaf growth points) is too large, the plant seems to be reaching towards the light.
- The lower leaves begin to turn yellow, the variegated ones turn green.
When someone doesn't have enough lightSource agardendiary.com
To get a reliable picture of illumination, measurements are taken using special instruments. For home use, a household photometer or lux meter (for example, RADEX LUPIN lux meter) is suitable. Household devices are easy to use; they will help organize optimal light conditions. An alternative solution could be a specialized application that can be downloaded from the Play Market or a similar store. It will take measurements using your smartphone camera.
If measurements show that the illumination level is almost normal, then there is no need to replace the lamps. The use of available artificial light can be maximized. Reflectors will help with this. They are made of metal (usually aluminum) with different coatings; They are available as floor-mounted or suspended, and significantly improve the quality of plant lighting.
Composite container with backlightSource architecturaldigest.in
About LED backlighting in the following video:
How to choose a lamp
Lamps for indoor plants ensure their active growth, especially in the autumn-winter period. Some representatives of the flora need longer daylight hours, so you need to turn on the lamps in the evening. For this purpose, different lighting elements are used: filament lamps, fluorescent, sodium, LED. They all have both their pros and cons.
Incandescent lamp
Incandescent lamps are rarely used for indoor flowers. This is due to the fact that they have high heat transfer and emit red, orange, and infrared rays. Under the influence of such light, representatives of the flora get burned, their sprouts become greatly elongated and also become thinner. Another disadvantage of filament lamps is their short service life.
Luminescent
Tubular light bulbs for indoor flowers with a white glow can be used for illumination, but the red waves in their spectrum are quite weak. They hardly heat up, but over time their light output decreases.
For lighting it is better to use phytoluminescent lamps. They are economical, compact, durable and safe. They have earned great popularity due to their selective spectrum and low heat transfer.
When using reflectors, the efficiency of tubular lamps increases by 25%.
Gas discharge
Sodium lamps emit bright light, last a long time, and are highly economical. However, they are more often used in greenhouses, as they are very bright (from 15,000 lux). There are not enough blue waves in their spectrum, so they are often combined with luminescent ones. Such devices are quite large, so they can illuminate a large area. The disadvantages include the high cost and the presence of mercury vapor in the flask.
LED
LED lamps are the best option for indoor flowers. They have high efficiency, energy efficiency, and durability (up to 50,000 hours). The dimensions of the LEDs are minimal, so they can be placed in hard-to-reach places (shelves, niches). They hardly heat up and are environmentally friendly. LED lamps emit red, blue, and orange light, which allows you to regulate the growth of indoor plants. Their only drawback is their high cost, but this is soon compensated for by saving electricity.
Briefly about the main thing
Houseplants often lack sunlight, so artificial lighting must be provided for them. To bring its parameters into line with the needs of indoor flora, you need to know what conditions a particular species needs.
An important parameter is the brightness (intensity, power) of the light flux. The spectrum emitted by the lamp is also important for plant development. There are warm and cold parts of the spectrum, and flowers need both of them at different periods of development.
To provide a suitable light regime, several types of lamps are used. For home gardening, fluorescent lights are a popular choice. You can find out whether plants are receiving enough light by their appearance, as well as using a household lux meter or a specialized application.
Why do orchids need lighting?
To understand why additional lighting is needed for orchids, it’s first worth remembering the basics of biology. Every plant needs an influx of sunlight, since nutrients in the leaves are synthesized only under the influence of UV rays. In the summer (when daylight hours are longer), ultraviolet light is sufficient for indoor plants. In winter, dawn begins late, and sunset, on the contrary, occurs earlier. Such changes can have a negative impact on most houseplants. Only shade-loving flowers feel good.
Don’t forget about some requirements for keeping orchids. This flower is native to the mountainous and forest areas of Africa, America, Southeast Asia and Australia. In the usual habitats of orchids, a hot climate with frequent heavy rains and plenty of sunlight prevails. This is where these plants do best, produce plenty of greenery, and bloom frequently.
In order for these flowers to grow well at home and delight the eye with bright buds, it is important for the gardener to create conditions that are close to natural. This means that if there is not enough sun, orchids may need lighting.
What kind of light do plants need most?
In order to explain this more clearly and clearly, let’s draw an analogy with something edible. Let's say you have a ripe peach, raspberry and pear on your table.
It doesn't matter to your stomach what you eat. It will digest all berries and fruits equally well. But this does not mean that there will be no difference for you later. Different foods still affect your body differently.
Eating 10 strawberries is not the same as eating 10 pears or peaches. You have to find a certain balance.
The same thing happens with light for plants. Your task is to correctly select how much of each light should be in the overall spectrum. This is the only way to count on rapid growth.
The most important question is which light will be considered the best? It would seem that there is no guesswork here. The best option is sunlight and its close analogues.
After all, for millions of years, plants developed under it. However, look at the picture below. This is what the intensity of sunlight actually looks like.
See how much green there is here. And as we found out earlier, although it is useful, it is not to the same extent as other rays. When they say that sunlight is the most effective and there is no need to deviate from Mother Nature, they do not take into account one simple fact.
In real life, not in experiments, plants adapt not only to sunlight, but also to the conditions of the environment in which they grow.
Let’s say that at the depth of a reservoir, where some greenery grows, blue color dominates. But in the forest under the canopy of trees, green comes out the winner.
Therefore, the opinion that sunlight is the best is fundamentally wrong. Here we need to talk more about the fact that it is the most versatile and is suitable for absolutely different conditions.
But in some cases, significant questions arise about its effectiveness. Here is the optimal distribution of spectra for our two most popular vegetables - cucumber and tomato:
Just these two elementary examples between a cucumber and a tomato clearly show how different their needs are. And if you illuminate both vegetables at once with the same light bulb, the results will be completely unpredictable.
Useful tips
Growing under full artificial light
It is not always possible to find a sufficiently lit place for an orchid. There are many examples of growing them entirely under artificial light.
What is important to decide:
- Set day and night temperature modes. They are important for many orchids. Especially for flowering; Orchid lighting option.
- Provide other conditions for the selected type of orchid: Humidity;
- Air circulation;
- And be sure to the power of the lamp and its distance from the flowers.
Solar lamp
It’s worth looking at such lamps in reality. Beauty in the garden becomes special. In the evening and at night. 5 pcs for 370 UAH. Great for the garden and home!
And the usefulness for orchids is a separate topic. And here we are not talking about frugality. About usefulness. For orchids, they do not provide the best spectrum for growth and flowering (red and blue). But you can count.
Installation recommendations
- It is necessary to install the lamp close to the plant itself, not forgetting about possible burns.
- When spraying plants, water should not fall on the lamp in order to avoid failure of the device.
- It is necessary to study the light regime of a particular plant. Daily lighting is required exclusively in the first days of seed germination.
Interesting articles:
- Do-it-yourself dog house layout, placement, drawings, manufacturing
- Making a water heated floor with your own hands: calculation and installation
- Wardrobe rooms: design projects, photos, how to make one in a small room with your own hands from a closet, layout and filling
- Bonsai pot features of Japanese pots Characteristics of models without holes Subtleties of choice
Light spectrum
The light spectrum is an important point in orchid breeding. In order for the plant to grow better, it is recommended to use devices that produce short-wave blue and long-wave red rays. To create such a light spectrum, a special device operating in combined mode is required. You can also purchase two devices that operate in red and blue modes, respectively.
It is worth remembering that the light spectrum changes throughout the day. To improve the synthesis of chlorophyll in green leaves, which is required for active growth and development, it is necessary that red rays hit the plant only in the dark. At other times, the flower needs blue rays.
Fertilizer
As for fertilizers, artificial feeding of the phalaenopsis orchid is not necessary, since the flower receives almost all the necessary elements independently from the environment. But if you want to be sure that your orchid gets everything it needs, you can also fertilize it with artificial fertilizers specifically for orchids, which you can easily find in flower shops.
When fertilizing, the main rule is the same as when watering - do not overdo it. Before feeding, the plant must first be watered with plain water, and then with water with fertilizer. Be extremely careful when fertilizing a flower while it is blooming, because if you overdose on fertilizer, flowering orchids may lose their flowers and buds, and sticky spots may appear along the edges of the leaves.
How to organize lighting?
When is it needed?
From October to March, all orchids need lighting, regardless of the location of the windows. Located on the north side - almost all year round. On the eastern and western sides during twilight, a little “additional lighting” is needed in spring and autumn. You can also provide additional light to weakened plants.
How to choose a device?
There are a large number of lamps on the market. The following are suitable for growing orchids:
- Special energy-saving lamps produced in the blue and red spectrum. Manufacturers guarantee that only 20% of the energy is converted into heat by the device, but they should not be placed close to the leaves. The minimum distance is 3 cm.
- Fluorescent lamps. Using gases such as mercury, they produce ultraviolet light, which is made visible by coating the lamp with phosphor. For orchids, devices with shades 33 and 840 are suitable.
- Metal halide lamps, also called gas discharge lamps. These devices can be of any shape; special models for growing plants are also available.
- Mercury gas discharge lamps work in the same way as fluorescent lamps, but have different markings. Choose those whose glow temperature is in the range from 3,200 to 200 K.
- LED lamps, otherwise known as light-emitting diodes, are considered optimal for floriculture. In stores you can find combination models with red and blue light with a ratio of 8/1 or 5/1 red and blue.
So what is the best lamp to illuminate orchids?
Special phytolamps that emit light at the required intensity and wavelengths are ideal. The most popular are fluorescent and LED. These are the best options for both amateurs and experienced gardeners. If you are a complete beginner, you can buy a regular energy-saving light bulb, but you shouldn’t expect any special effect from it, so it’s still better to install an inexpensive LED lamp.
If you are an amateur and you only have one or two flowers, there is no need to spend money on a special paw; an energy-saving one will suffice. And to keep a large number of exotic orchids you will need professional lighting.
What color should the rays be?
Light with long red and short blue waves is preferred for orchids. You need to buy either one lamp that combines both of these spectra, or separate ones - red and blue. In the second case, the blue one is turned on throughout the day, and the red one at dusk.
Installation
There are several options for lighting orchids:
- For a small window sill, an office lamp with a screw mount or a clothespin is suitable.
- For a dozen low orchids, compact fluorescent lamps located above the foliage are suitable (photosynthesis practically does not occur in flowers, there is no point in lighting them). You can attach them to the underside of a shelf or a window crossbar. Help! It is better to combine the first and second types of lamps with reflectors - this way more light will fall on the flowers. For this purpose, you can use not only special reflectors, but also an ordinary mirror.
- If you have a winter garden, you will need high-quality ceiling lighting with gas-discharge lamps of at least 250 W of power.
Below is a visual video about lighting for an orchid using pendant lamps:
Duration
Orchids are accustomed to long daylight hours, on average up to 12 hours. Specific lighting standards are individual and depend on the orchid variety. The minimum time frame is 10 hours, the maximum is 16.
Effect on the plant
Properly installed lighting has a positive effect on the plant, causing the growth of green mass and increasing flowering. In winter, artificial light will prevent the plant from falling into a dormant state, which will cause it to bloom more often.
Orchid on the west window
The western window, although not as sad for the orchid as the northern one, is also not ideal. In summer, the sun appears there for a few hours and only in the afternoon, and in winter it does not appear at all. Therefore, if the free window in your apartment is oriented to the west, you also cannot do without additional lighting.
Regardless of which window your orchid is placed on, its leaves should not be allowed to come into contact with the glass. Even the slightest cold can destroy a plant, and leaves stuck to cold glass will suffer severe frostbite within a few hours and will soon fall off.
Features of keeping orchids at home
Let's find out in more detail what kind of lighting orchids like: light or shadow. In order for the flower to safely grow roots and foliage, and to grow a peduncle with a large number of buds in due time, you need to find a place in the apartment where there will be a lot of sunlight .
For an orchid in an apartment you need to find a place that will be well lit.
But at the same time, the lighting should be diffused, since direct sunlight, even in winter, can burn the leaves of the flower.
IMPORTANT! If the room has only south-facing windows, then the flower is placed 2-3 m from the window.
Follow these 9 rules and your orchid will bloom all year round
Looking at a blooming orchid, many gardeners don’t even think about whether to buy this extraordinary plant or not. Of course, buy! But will it bloom just as well at home?
Everyone knows that an orchid is a rather capricious plant and requires meticulous care. You can achieve repeated flowering from it if you know all the factors that contribute to this and follow a certain care regimen. Then the orchid will bloom for 2 to 6 months. And some genera, like phalaenopsis or vanda, can bloom all year round.
For an orchid to bloom...
The frequency of orchid flowering depends on compliance with certain care rules. In order for a plant to bloom, you should remember 9 important conditions that contribute to this.
1. Find out the age of the orchid
If you bought a non-flowering plant, and it is in no hurry to please with flower shoots, perhaps it is still too young. Different types of orchids bloom at the age of 1.5 to 3 years. To determine that an orchid is old enough, you need to count the number of shoots. An adult plant ready to flower should have from 5 to 8. If flowers appear on an orchid earlier, this is not always good. The fact is that a plant that is too young may not have enough strength to recover after flowering, and the orchid may die.
2. Don't move the potty
Many people know that moving is a real stress for an orchid. But this flower does not like even minor movements. The orchid reacts to its position in relation to the light. Therefore, if there is a need to rearrange a pot with a plant, it is necessary to place it with the same side to the light source as it was before. Also, do not move the orchid while watering. Movement adversely affects the growth of the flower, especially at the moment the peduncle appears.
3. Pay attention to the roots
As you know, orchid roots are actively involved in the process of photosynthesis, so it is important to ensure that they have enough light. Since it is not recommended to move the orchid again, it is worth taking care of the roots in advance. For example, instead of ceramic pots, it is better to use transparent plastic containers with plenty of drainage holes. It is not recommended to use containers with corrugated walls for planting this flower, since its roots tend to grow to uneven surfaces. In addition, sharp edges and elements can injure the root system, which will harm the entire plant as a whole.
4. Take care of lighting
Sunlight is a very important factor affecting the flowering of an orchid. Without full daylight (10-12 hours a day), these plants will not bloom. Therefore, in autumn and winter, when there is very little natural light, flowers should be illuminated with lamps.
Phytolamps are special lamps designed to illuminate plants: they provide a lot of bright light without drying out the air around the flowers.
If an orchid produces a peduncle in autumn or winter, care should be taken to ensure that it does not die due to the short daylight hours. Without additional lighting in the dark season, the peduncle may stop developing or dry out. If it is not possible to illuminate the entire plant, it is enough to provide illumination only for the tip of the peduncle. The main thing is to make sure that neither it nor the plant itself gets hot.
5. Ensure acceptable temperature differences
The catalyst for flowering of many types of orchids is a slight difference between day and night temperatures. Therefore, for an orchid to bloom, the temperature at night must be 4-6°C lower than during the day. Of course, creating such conditions throughout the year can be problematic. But from late spring to early autumn, orchids can be kept outdoors, where the temperature difference is achieved naturally. In cooler times, when flowers should already live at home, rooms with orchids need to be ventilated. Just do this very carefully, remembering that these plants are very afraid of drafts.
6. Water your orchid correctly
You need to water the orchid after the soil dries out - this will make it possible to avoid rotting of the roots. These requirements apply both in summer and winter and apply to both children and adult plants. However, there are some exceptions here. After the orchid has faded, watering should be reduced by about a month.
In nature, after flowering, orchids begin to set seeds, which should scatter in different directions for several kilometers. This is only possible during dry periods, but not during the rainy season. Therefore, it is necessary to provide the orchid with conditions that are as close to natural as possible - then the flower will grow healthy and bloom often.
Before and during flowering, the orchid requires more intense watering than usual. Further, during the dormant period, specimens with hard leaves and the presence of pseudobulbs should be watered according to the basic principle (after about 10-12 days).
7. Humidify the air around the plant
Another important condition for flowering is air humidity. If there is not enough of it, the orchid may stop growing or unopened buds and flowers may dry out prematurely.
To increase the humidity in the room where the orchid grows, you can place a plate of water next to the flower. Also, during very dry periods (when the heating is turned on in houses), the plant should be sprayed. Suitable humidity for orchids is 60% and above.
8. Choose the right fertilizers
To feed orchids, it is recommended to use formulations based on phosphorus and potassium, as they stimulate the appearance of flower buds. In addition, the use of such fertilizers ensures that the plant produces healthy and strong flowers. But it’s better not to get carried away with nitrogen-based fertilizing: this element, on the contrary, inhibits the development of flower stalks.
9. Don’t be afraid to “scare” the plant
Sometimes, to make an orchid bloom, it needs to be given a little stress. It happens that all the conditions for flowering are met, but the flower stubbornly refuses to shoot. This sometimes happens because the orchid is doing too well. In this case, the plant directs all its energy to the growth of green mass. One way to stimulate flowering is to “shock” the orchid a little: reduce watering or move the plant pot to a cooler place.
Dormant period in orchids
After flowering, the orchid enters a period of rest, when it begins to accumulate strength for a new flowering. Care at this time is no different from care during other periods. The flower still needs good watering, high humidity, sufficient lighting and regular prevention against diseases and pests.
As for fertilizing, their frequency and volume during the rest period should be reduced. If there is a need to replant an orchid, then the time to do this procedure is now, when the plant no longer blooms.
Replanting is necessary if roots are sticking out of the drainage hole, or the soil dries out quickly after watering. As a rule, the need for this procedure appears after 2-3 years.
Are orchids suitable for cutting?
What could be more beautiful than a bouquet of orchids? But these flowers do not live long, and not every species is suitable for cutting. Let's try to figure out how to extend the life of an epiphytic bouquet and which orchids to choose.
Phalaenopsis, cymbidiums and paphiopedilums can stand in a vase and retain freshness and aroma for several weeks (and sometimes even a month). Other orchids risk not standing for even an hour, literally withering before our eyes.
If you purchase cut orchids, look first at the petals and sepals. They should be shiny, as if covered with wax, and hard - then the orchid will last a long time.
How to extend the life of a bouquet of orchids:
- If the flowers were brought from the store, then their cuts need to be updated. The stems should be cut at an angle. It is recommended to carry out the procedure under running water. It is advisable to update sections every 2-3 days.
- The water for keeping cut orchids should be soft and clean: you can use boiled or filtered water. It needs to be updated periodically by adding fresh water.
- Cut orchids, as well as potted home orchids, are afraid of too high and very low temperatures. It is also recommended to protect them from drafts and bright sun.
Source
positiveno.me