Phalaenopsis and Paciopedilum are among the most common types of orchids that are in high demand among buyers and gardeners. So, having studied the basics of caring for them (watering, pruning, replanting, fertilizing, installing supports), the gardener will receive a healthy and beautiful flower for sale, at a high price!
In its homeland in Asia, this orchid grows in humid tropical forests in soil rich in humus. Therefore, it does not need storage organs such as pseudobulbs, which many orchids have. But it is very sensitive to lack of moisture.
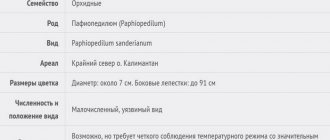
- Growth type: sympodial without pseudobulbs
- Temperature: for the general group: 15-20 °C during the day, 10-15 °C at night; for spotted and multi-flowered: 18-27 °C during the day, 16-21 °C at night
- Daily temperature changes: 10-11 °C (general); 5-6 °C (spotted and multi-flowered)
- Flowering duration: 6-10 weeks
- Flowering time: autumn, winter, sometimes spring (new speciesA species is an evolutionarily established set of individuals, characterized by a single...)
- Flowering frequency: from 8 months to 1 year
- Flower color: white, yellow, pink, purple, brown, green
- Place: a window facing north or east, or west, but with transparent curtains.
Paphiopedilum orchids are divided into three groups according to morphological characteristics:
- general, with a large flower, often the only one on the peduncle, and green, usually shiny leaves;
- spotted, with leaves of different shades of green, with a single oval-shaped flower on the peduncle;
- multi-flowered, the flowers have colorful colors and bloom on a single peduncle.
Location and support
Paphiopedilum is quite light-loving, but prefers diffused rays to direct sunlight. Place the plant on the windowsill so that the top of the pot is well lit, turn the pot with young shoots towards the glass. Place a tray with large, constantly wet expanded clay under the container.
If the lighting is too intense, the orchid will “give a signal”: the color of the leaves will first become olive, and then they will quickly turn yellow.
Paphiopedilum is most often sold with supports. After purchasing the plant, the support should be left, as it helps the peduncle not to break due to the weight of the flowers.
Here's what to do:
Mix the ingredients at a rate of five parts fir bark to one part each of the other two ingredients. If your orchid is potted with sphagnum moss or tree fern fiber, you'll probably be best off potting it into bark. This is the preferred medium for full-sized orchids as it protects the roots from rotting. Mini orchids do better with moss, fiber or coir.
With full-size specimens, even if you water very infrequently, it is better to use light, airy bark than materials with high water-holding capacity. Orchids are very drought-resistant, but do not tolerate wet roots.
Pruning and watering
When all the flowers have withered, trim the flower stalk with pruning shears slightly above the base to avoid damaging the leaves. The remaining part of the peduncle will subsequently dry out and will be easy to remove.
Before watering, to avoid plant rotting, remove yellowed leaves. To do this, cut them lengthwise into two parts and carefully pull them out, holding the plant with your other hand so as not to accidentally pull it out of the pot.
Make sure the substrate is kept moist at all times. Check the humidity with your finger, dipping it 1-2 cm into the substrate. Water the plant regularly with soft water, preferably in the morning. Make sure that water does not get on flowers, young shoots and leaves. Paphiopedilum is very susceptible to decay.
Maintain a comfortable temperature
Phalaenopsis is an ideal choice as a flowering houseplant because it thrives at normal room temperatures. If your home is warmer than 16 degrees at night and 21 to 28 degrees during the day, your orchid will be happy.
Avoid exposing the plant to temperatures below 16 or above 35 degrees. Remember that the temperature near windows and doors may differ from the temperature in the rest of your home, so position your phalaenopsis plants accordingly and monitor the temperature closely. If your plant is located near a door that receives frequent exposure to hot or cold air during the day, it may drop buds due to temperature fluctuations. When this happens, the buds fall off without opening.
Fertilizer and replanting
It is preferable to use liquid fertilizer for indoor decorative foliage plants. The dose should be half that recommended on the package! Fertilize your orchid every 15 days. Stop doing this when the young leaves reach the same size as the old ones and new flower stalks appear.
In order for orchids from the first group to bloom, they must be kept outdoors from June to September. SpeciesA species is an evolutionarily established set of individuals, characterized by a single ... from the group of spotted and multi-flowered ones, they do not need the coolness of the night to bloom, but they can also be outdoors in the summer - in the garden or on the balcony.
Once a year, not in winter and not during the flowering period, but during the formation of new shoots, paphiopedilum can be replanted. Carefully remove the orchid from the pot and free the roots from any remaining substrate. Carefully examine the roots and remove damaged or rotten ones with pruners. The instrument must be previously disinfected.
Place drainage at the bottom of the pot. Then fill the pot with substrate. The substrate level should be 1-2 cm below the edge of the pot. Distribute the plant evenly. Gently straighten the roots.
Composition of the mixture: 10% medium-fraction expanded clay, 30% sphagnum and 60% medium-sized pine bark. Be sure to moisten the mixture before use.
Pour the mixture into the pot and tamp it down with a stick. Before new shoots appear (after 3-4 weeks), do not water the orchid, but simply spray the surface of the substrate with water daily.
Kinds
To support the flower, you should use a stand.
In general, the species differ from each other in the sizes and colors of the inflorescences, and there are also species with more expressive features.
For example, phalaenopsis mix has several (usually 2) peduncles, they are not much higher than usual. However, this species blooms somewhat less than others, about 1-2 months.
Phalaenopsis ambonensis. This species is distinguished by a short stem, but the leaves, on the contrary, can reach a length of 30-40 centimeters, the flowers have a diameter of up to 6 centimeters. The flowers bloom slowly, one after another, so the flowering period is quite long.
Phalaenopsis rider, also called Phalaenopsis mini. The plant itself is not very small; the leaves can reach a length of up to 20 centimeters. But the flowers of the plant are small, only 1-2 centimeters in diameter; the flowers form rather dense inflorescences. Also, this type is distinguished by a rich variety of colors.
Phalaenopsis Maria is one of the most interesting and rare species. This type of phalaenopsis differs in leaf color. In addition to the white and pink tones, there are yakri, pink and red spots on the petals.
Reproduction
The largest speciesA species is an evolutionarily established collection of individuals, characterized by a single ... produce up to two new shoots at the same time, which appear either during or after the flowering of the plant. The oldest leaves usually do not die back until the next bloom.
Divide the large plant into two parts with your hands. In this case, one new shoot should remain in each of them. Plant divisions in the substrate (see advice on page 151) and spray its surface with water until new roots appear.
So what's the difference?
Phalaenopsis (lat. Phalaenopsis) belongs to a genus of epiphytic plants from Southeast Asia. In nature, it lives in humid plains and mountain forests. This tropical plant got its name thanks to the director of the botanical garden, Karl Blume, who confused it with a butterfly. The word “Phalaenopsis” is translated from Greek as “Moth-like” .
These flowers are very beautiful and dearly loved by orchid fans. Phalaenopsis belongs to the orchid family, but they themselves represent a separate genus of plants. They are on a par with such genera of orchids as Vanda, Dendrobium, Cymbidium and others.
Thus, to the question whether this plant can be called an orchid, there is a completely clear answer: yes, you can, there will be no mistake. However, a more accurate definition would be the genus name.
The words “orchid” and “phalaenopsis” can be synonymous from a biological point of view: the genus has all the features of the orchid family. In other words, all phalaenopsis orchids are orchids, but not all phalaenopsis orchids are phalaenopsis.
What distinguishes phalaenopsis from other orchids is the following::
- Unpretentiousness. The plant does not require special attention and will be a good option for beginning gardeners.
- Moist air tolerance.
- There is no need for temperature changes during breeding.
- There is no need for dense and heavy soil. For Phalaenopsis, the soil serves as a support, nothing more.
Phalaenopsis
In 1980, it became possible to clone this orchid in vitro. Since then it has become very common due to its luxurious flowers and long flowering period. This orchid easily adapts to home conditions.
- Growth type: monopodial
- Temperature: 22-30 °C during the day, 18-25 °C at night
- Daily temperature changes: 2-5 °C
- Flowering duration: 2 months minimum, sometimes longer
- Flowering time: all year
- Flowering frequency: variable
- Flower color: everything except blue
- Place: east or west window.
How to propagate?
The most optimal method of propagation is transplantation with lateral shoots (“babies”):
- wait until the roots appear on the “babies”;
- carefully cut off the shoot from the main shoot with a sharp blade;
- plant it in a small container.
Caring for a small shoot is no different from caring for an adult orchid.
Location and support
Phalaenopsis needs a high, but not excessive level of substrate moisture, so its roots, if there is a lack of moisture, extend beyond the pot to absorb water from the air. Place the container with the plant on a tray with wet expanded clay. Place a grate between the pot and the expanded clay to prevent the drainage holes from becoming clogged.
Transparent containers are suitable for phalaenopsis. They are convenient because they make it easy to check the condition of the roots; if they suddenly begin to rot due to excess moisture or shrinkage of the substrate. If you notice damage, you need to replant the plant.
The pot should be selected so that its diameter is two fingers wider than the pot, and its height should be 5-6 cm greater. In this case, the edges of the pot and the flowerpot should match, so take a soft mesh, roll it up and place it under the pot to raise it a little.
In order for the container with the plant to become more stable, the peduncle will need support. Bury the support into the substrate in close proximity to the peduncle without damaging the roots. Attach the support to the peduncle in two places using clips. The support should be installed before the buds bloom, as flowers fade faster if their position is changed after blooming.
Planting "Butterflies"
Orchids Butterflies are planted in transparent pots or special “crowns” for orchids. This is due to the characteristics of their root system, which needs light and air.
The clear pot can be replaced with any other clear plastic container, depending on your preference.
The crown is approximately the size of a pot. However, instead of blank walls, there is a kind of fence around its circumference. It is designed to hold the substrate inside the structure. At the same time, air circulates freely inside, and the roots grow in a more natural environment for them.
Instead of regular soil, a substrate is poured for the Butterfly. It usually consists of tree bark. May also contain coconut fiber, moss and charcoal.
When planting, the substrate in the pot is placed freely, without compacting or tamping. The root collar is not buried.
Pruning and watering
When the plant has completely bloomed, cut the flower stalk at the level of the 2nd or 3rd thickening from the base of the plant. In 80% of cases, one of these thickenings (nests) will produce a new peduncle after two or three months. After secondary flowering, trim the peduncle at the very base.
Dried leaves of phalaenopsis do not need to be removed, because they fall off on their own.
Once a week, water the orchid with soft water at room temperature, the volume of which should be equivalent to the volume of the pot. Leave for a few minutes, then drain the excess water and place the plant in the pot. Do not leave the substrate dry: the fleshy leaves should not become soft between two waterings.
If the leaves begin to yellow and dry out at the base of the plant, this is normal. Phalaenopsis should not have more than 4-6 leaves at a time. As new leaves grow, the oldest ones die off. rain moisture enters.
When watering or spraying, water from the watering can should not fall on the flowers and leaves so that they do not rot. During the hot season or winter, if the room is very heated and the air is dry, spray the back of the leaves with soft water at room temperature, especially for miniature species.
Features of flowering
Phalaenopsis begins to bloom at the age of 2.5 - 3 years.
Do not try to stimulate flowering before this. This has a negative effect on the plant.
It can be difficult to recognize the beginning of the process - on the stem, in addition to the peduncle, adventitious roots can form. They can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- the peduncle has a pointed tip, scales appear in the embryonic stage.
- the adventitious root has a blunt tip, the surface is smooth, without scales.
On some plants, buds appear almost simultaneously (this is most often found in pink species). In others (white species), the lower buds open first, then the upper ones, as a result of which the flowers on the orchid are present for a longer time.
With proper care, flowering can last up to 8 months.
Stimulating flowering
The more the daytime temperature differs from the night temperature, the faster the phalaenopsis blooms. In addition, flowering can be stimulated by a stressful situation:
- Stop watering for 10 days;
- then lower the pot into warm water for a quarter of an hour;
- after which they feed.
Recommendations
The frequency and volume of fertilizing must be reduced.
At the initial stage, it is not recommended to move the pot from place to place or replant.
If roots begin to protrude from the drainage holes and look diseased or damaged, or the soil becomes compact and dries out quickly after watering, you may want to repot.
Pruning after flowering
Only completely dried flower stalks need to be trimmed.
The flower stalks of the plant dry out after flowering. They must be removed and the cut area covered with wax or plasticine.
If only the top has dried, cut off only the dried part. Buds may still appear on it.
Attention! It happens that there is some pause between the drying and falling of the first buds and the development of the second. Therefore, do not remove the peduncle until you are sure that new buds will no longer develop on it.
Fertilizer and replanting
Throughout the year, with the exception of the period between the flowering of the plant and the appearance of new shoots, add special fertilizer during watering once - from spring to autumn and twice - in winter.
To encourage secondary flowering, add a special fertilizer for flowering orchids from the end of the growing season until new leaves emerge after flowering.
Phalaenopsis does not need regular replanting. Only if the roots have filled the entire pot and signs of decay are visible, in the spring or summer, after flowering, carefully remove the plant from the pot. Free the roots from any remaining substrate.
Do not cut off aerial roots, even if they seem dry. In fact, they function normally. Remove dry or rotten roots with sharp, disinfected pruning shears. Trim them as close to the base as possible. After this operation, disinfect the pruning shears again.
The substrate for phalaenopsis should consist of 80% medium-sized pine bark and 20% medium-sized expanded clay. You can add a little sphagnum to increase the moisture capacity of the substrate, but in this case, be careful not to overwater. Moisten the mixture before use.
Take a pot slightly larger than the previous one and fill it with the wet mixture (see tip above). The level of the filled substrate should be 2 cm below the edge of the pot. Place the plant in the center. Add the substrate so that the base of the plant - the neck - remains above its level. Tamp the mixture with a stick from time to time. Do not water the orchid until new shoots appear (after 2-3 weeks). It is enough to spray the surface of the substrate with soft water at room temperature (avoid getting water into the core of the plant).
Care after purchase
Phalaenopsis purchased in a store must be created with comfortable conditions for normal adaptation and adaptation to a new location:
- the flower is not watered for several days (with the exception of plants planted in too dense or dry soil, which can be watered with warm boiled water);
- Phalaenopsis is not sprayed or fed for 10 days;
- for a week they are provided with a location on a window with diffused sunlight, then they are placed in a permanent place.
If Phalaenopsis is located evenly and steadily in the container, the substrate meets the recommended standards, the root system and leaves look healthy, then the flower can be left in a store pot for a long period (up to 2-3 years).
Reproduction
Not only flowers appear on the peduncles of phalaenopsis, but also young shoots with leaves and roots, with the help of which the orchid can be propagated. The appearance of babies is usually due to excessive application of nitrogen during fertilization or the fact that the plant has weakened.
Some speciesA species is an evolutionarily established collection of individuals, characterized by a single... this orchid is slightly more predisposed than others to reproduce “copies of itself” in this way. Sometimes, if the plant is very weakened, it may sprout at the base of the leaf rosette. It can be separated at the time of transplantation.
When the roots of the sprout reach 12-15 cm in length, separate them with a sharp, disinfected knife and immediately plant them in the substrate.
Orchids thrive in high humidity
Phalaenopsis are epiphytic orchids, which means they collect a lot of moisture and nutrition from the air around them. During hot, dry weather or during the winter months when it's hot, your plant will need extra moisture. This is easy to achieve. Simply place the orchid pot on a layer of pebbles in a drip tray. Pour in some water, but make sure the water does not touch the bottom of the pan. Constant contact with water will cause root rot. The water in the saucer will gradually evaporate, creating a small wet area around your plant. Be sure to check the water level in the drip tray regularly and add water as needed.